Tooth depulpation is an endodontic manipulation to remove the neurovascular bundle from the tooth cavity and/or tooth roots. When is tooth removal necessary?
Depulpation of diseased teeth is carried out when the dental pulp is inflamed, due to the penetration of caries through the walls of the tooth to the intrapulp chamber. Through the carious gap created in the enamel and dentin, microbes and toxins enter the pulp, and the death of nerve fibers and capillaries of the pulp begins. Severe pain occurs when the tooth comes into contact with temperature and chemical irritants, i.e. for cold, hot, sour, sweet, etc.
Depulpation of teeth for prosthetic purposes
For grinding for a crown or dental bridge, the teeth are first depulped. High-quality depulpation (depulpation) of intact teeth allows you to avoid inflammatory processes (cysts and granulomas) under the root of the tooth on which the crown is installed. A non-pulp tooth under a crown can cause severe pain due to inflammation of the pulp.
How does pulp removal occur?
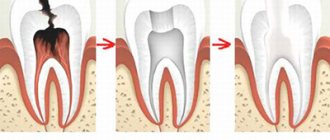
The process of depulpation allows you to stop the penetration of infection from the crown and root parts of the tooth under the apex, behind the root of the tooth, into the bone tissue surrounding the tooth. Thus, timely tooth depulpation prevents complications such as periodontitis , cysts or dental granuloma from developing. There are complete removal of the tooth pulp (from the roots and from the coronal part of the tooth) - pulp extirpation, and incomplete removal of the pulp (only from the coronal part of the tooth) - pulp amputation. Pulp amputation is carried out in the initial stage of pulpitis in order to preserve viable pulp in the root canals of the tooth.
What is depulpation and what is its essence?
What does tooth depulpation mean? Let's break the word down into parts - “de” means “removal”, and “pulp” refers to the soft neurovascular bundle that is located inside the tooth cavity and in the root canals. That is, depulpation or depulpation is the removal of the so-called “dental nerve”. After which the “empty” areas are filled with filling mass or pins, and then closed with crowns, inlays or special fasteners for dentures. Depulpation[1] is irreversible, i.e. a new pulp does not form in place of the removed one. Dental tissues cease to receive nutrition from the inside, and the tooth itself is considered “dead.” But this does not mean at all that it will fall out soon.
Any dentist should be able to carry out this procedure, but in the field of work this is most often done by dental therapists or more specialized specialists - endodontists. That is, if a patient comes to an orthopedist for a prosthesis, then if pulp removal is necessary, he will refer the person to a dentist-therapist.
What is the procedure
Depulpation is a dental procedure in which the pulp, the neurovascular bundle of the tooth, is removed. The pulp ensures the vitality of the tooth and, in particular, its sensitivity due to the large number of nerve endings. Depulpation is a complex dental procedure that can cause severe pain. After depulpation, the tooth actually dies, since metabolic and restoration processes no longer take place in it, but retains its chewing function.
What is the purpose of depulpation?
The goal of the procedure is to achieve several important results that will allow the patient to wear the prosthesis for a long time. Moreover, during the entire period of wearing the person will not be bothered by pain and the need to remove, for example, a crown. Let's take a closer look at what effect should be achieved:
- the pulp will not overheat during grinding of the stump and, accordingly, will not become inflamed (i.e., pulpitis will not appear under the crown),
- cariogenic bacteria will not penetrate into the pulp (i.e., pulpitis is again excluded),
- It will be possible to place pins or a core inlay into the canals: this will strengthen the restoration, i.e. it will last longer.
Don't know what type of prosthetics to choose?
We will help in the selection, advise where to read more information and compare types of prosthetics.
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor in Moscow clinics is free! Call now or request a call
Working hours: from 9:00 to 21:00 - seven days a week
When a nerve must be removed - indications
Whether tooth depulpation is necessary before prosthetics or not, only a doctor can say after a thorough examination - instrumental and x-ray. Mandatory removal of the dental nerve is necessary for the following indications:
- there are signs of pulpitis, i.e. inflammatory process of the pulp: pain, darkening of the deep layers of dentin,
- the top of the tooth is severely damaged,
- the natural crown has massive fillings,
- the patient often experiences relapses of caries,
- it is planned to install a crown with thick walls (for example, metal-ceramic): in this case, it is necessary to sharpen the stump quite strongly, which will lead to thinning of the dentinal layer (i.e., the pulp underneath will be less protected) and to its potential overheating during treatment with a drill. As a result, if depulpation is not performed, the risk of pulpitis increases and the time for re-prosthetics approaches.
Stages of the dental nerve removal procedure
The doctor chooses a specific treatment plan depending on the clinical picture. Therefore, first you will undergo a complete examination. An x-ray is required. The image clearly shows the affected nerve, the location of the source of inflammation.
One of the symptoms of pulpitis is severe pain, which, if the disease is advanced, can innervate other areas of the jaw. Without an x-ray, it is impossible to determine exactly where the inflammation is and which tooth needs to be depulped. Also, using the image, the doctor assesses the condition of the pulp. This will help you decide whether the nerve will be removed completely or partially.
When the nerve of a tooth is partially removed, its coronal part is excised. In this case, the root part of the pulp is preserved. Partial resection allows you to keep the tooth alive, since the remaining part of the pulp will provide blood supply and nutrition to the tissue. Despite the fact that the method allows you to save part of the nerve, it is rarely used.
Most often, the nerve is removed completely. In case of severe inflammation, this method allows you to save the tooth. It can be restored and used as a support for prosthetics.
The nerve removal procedure will require several visits to the dentist. The procedure during each visit also includes several stages:
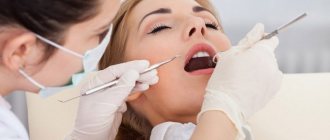
- Anesthesia. The nerve is removed under local anesthesia. The doctor injects an anesthetic and numbs the area of the gum where the diseased tooth is located. Anesthesia is selected individually to eliminate the risk of an allergic reaction during treatment. If you have an allergy to anesthetic drugs, tell your doctor. He will select a drug for you that is completely safe for your health. Thanks to the use of modern anesthesia, nerve removal in our clinic takes place with virtually no pain.
- Preparing the oral cavity. After the anesthesia has taken effect, the doctor isolates the surgical area using a rubber dam. This is necessary in order to prevent saliva from entering the operated area. Along with saliva, an infection can get into the wound, which can lead to a relapse. Careful isolation of the surgical area will help reduce possible risks.
- Treatment of dental canals. Before removing the nerve, all damaged tooth tissue must be carefully removed. To do this, it is drilled out using a drilling machine. The doctor will also open the pulp chamber.
- Nerve removal. Traditionally, nerve removal is done using a pulpoestrator. This instrument allows you to capture the pulp through the exposed pulp chamber. After the doctor grabs the nerve bundle, he will remove it from the dental canal. You can extract the nerve in another way: using a special miniature tool - a file. Visually, this tool looks like a long needle, but has a rough surface and therefore, in essence, is a miniature saw. Unlike a pulp extractor, the file allows you to carefully cut off the nerve bundle. Its use reduces the risk of damage to healthy tooth tissue. The doctor will decide which extraction method to choose based on the anatomical features and clinical picture of the patient. The entire procedure for removing the tooth nerve is controlled instrumentally, using an electronic apex locator device. It displays an image on the screen that clearly shows the position of the instrument. Using electronic devices, the dentist receives information about the number of dental canals, their shape, and length. Instrumental control helps the dentist perform the operation with high precision. This also reduces the risk of insufficient cleaning of the canals and re-infection.
- Treatment of dental canals. After extraction of the nerve of the tooth, it is necessary to treat the dental canals. First, they are cleaned to remove remnants of nervous tissue and foci of infection. Cleaning is done with files of different diameters. Cleaning begins with the use of the smallest diameter tool. During the procedure, the doctor performs rotational movements, gradually moving downward. To remove sawdust, the dental canal is washed with a syringe with an intracanal needle. Then the manipulation is repeated several more times using files of larger diameter.
- Temporary filling. The cleaned channels are expanded and washed with antiseptic solutions. To completely destroy the source of inflammation, a drug is placed into the cavity. After the procedure, a temporary filling is installed.
After completing the first stage of treatment, the doctor will set a date for re-examination and appointment. Before making a permanent filling after removing the nerve of a tooth, you need to make sure that the inflammation has completely stopped. To do this, another x-ray is taken. If the image shows that the nerve removal was successful, a permanent filling is made. The seal must be completely sealed. This will eliminate the risk of infection in the future.
Gutta-percha is used for filling. This is a rubber-like material that the doctor inserts into the canal cavity. Filling after nerve removal can be done in different ways:
- Thermafil and lateral condensation. These methods are used if there is good access to the operated tooth. Using special instruments, the doctor inserts a flexible pin-cone into the cavity.
- Thermogutta-percha. This is a more effective method that allows you to hermetically seal teeth with multiple and complex root canals. Thermogutta-percha is a moving mass, so it fills not only the main channel, but also microchannels, the smallest cracks and defects. It is difficult to achieve such tightness using traditional filling methods.
High-quality hermetic filling of the canals after removal of the nerve allows you to preserve the root of the tooth, so that it can be restored in the future. Filling material that fills all cavities becomes a reliable barrier against the penetration of pathogenic microflora, and this reduces the likelihood of re-infection.
When can you do without deletion?
Let's consider situations when depulpation can be abandoned, i.e. do not perform it before prosthetics:
- the stump (ground tooth tip) has thick walls,
- the pulp is not inflamed,
- in the future there is no risk of caries/pulpitis under the denture,
- overheating of dentin and pulp is excluded.
For veneers and restorative inlays, you can, in principle, do without depulpation altogether, as well as for thin ceramic crowns - but only if all the requirements just outlined are met.
Contraindications to the procedure
Contraindication is children's age. Or rather, a milk bite - here it is forbidden to go through root canals with instruments, because... the developing rudiments of permanent teeth can be damaged. Intolerance or prohibition of the administration of anesthesia is also a contraindication. As well as serious mental disorders, when a person can unknowingly harm himself during dental procedures.
Read on the topic: indications and contraindications for installing dentures.
How is the procedure performed?
How is tooth depulpation done? It is carried out in at least 2 visits to the clinic. In one visit, removing the pulp and immediately placing a filling or pin can be dangerous because if pathological areas remain in the cavities, then over time inflammation will develop under the prosthesis. Next, we will consider how depulpation occurs and what stages are included in it.
First visit to the doctor
First of all, the patient is given an x-ray to find out the condition of the pulp and the presence of inflammation under the roots. Then they give a “freezing” injection with an anesthetic. To remove the pulp, the dentist needs to drill out part of the hard tissues - enamel and dentin. First, the pulp is removed from the pulp chamber. And then, using special endodontic instruments, you will need to remove all the loose pulp from the canals. After this, medicine is put inside and a temporary filling is placed, which lasts for an average of 7-14 days. During the process, you need to take an x-ray to assess the quality of the work. And in the most modern clinics, canals are treated under a microscope.
If the pulp is removed using arsenic paste, the treatment technology is different. Anesthesia is not required here, because... it does not hurt. Paste is placed into the cavity and closed with a filling. After 2-3 days, the patient must return to the clinic, because... It is during this time that arsenic will “kill” the pulp bundle and may begin to negatively affect healthy tissue. If the filling falls out or is damaged, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Second visit to the dentist
At the second appointment with the doctor, the medicine or arsenic paste is removed, the canals are processed, dried and sealed. Next, you again need to take an x-ray to assess the quality of the filling and the absence of “empty” areas. The patient is sent to an orthopedist, where the doctor will unseal the canal a little and place a pin, stump tab or attachment (lock) for a removable denture into it, and then take impressions for a crown or other orthopedic structure.
The appearance of pain and its causes
Why does a tooth hurt after pulp removal? Soreness often occurs after the anesthetic injection wears off. Pain after the procedure occurs for several reasons - normal and pathological. Here you need to understand the nature of the pain and what it is talking about.
For example, if the pain is tolerable or can be easily eliminated with painkillers, if it weakens every day, then this is a variant of the norm. After all, during the passage and expansion of the channels, healthy tissues were slightly injured, and pain is a natural reaction of the body. How long can a tooth without a nerve hurt after the procedure? On average, the discomfort goes away completely in 7-14 days. But in some patients it persists for 4-6 weeks and then disappears.
Read on the topic: what to do if a tooth hurts under a crown - causes of pain and methods for eliminating it.
The pathology is considered to be severe pain for several days, which is practically not relieved by pills. And also the reappearance of pain a few days or weeks after a period of painlessness. Symptoms such as severe redness and swelling of the gums, fever, headache, and bad breath should alert you. These signs most likely indicate that the depulpation was carried out incorrectly and inflammation began under the prosthesis. Or aggressive caries develops under the crown. Dental care is needed here, otherwise complications may arise - periodontitis, for example.
Causes of dental pulp damage
The dentist is often visited because of caries - damage and destruction of enamel, which at the initial stage causes aesthetic discomfort.
Important: if the disease is started, the process affects the deeper layers of the tooth and pulpitis develops, that is, the neurovascular bundle becomes inflamed.
Pathologies arise due to the rapid proliferation of microbes, but in addition, the pulp can be damaged for the following reasons:
- gum disease, in which the neck of the tooth is exposed, the bone tissue is destroyed and harmful bacteria penetrate inside;
- trauma, as a result of which part of the tooth can break off, and then microbes enter the resulting cavity;
- mistake by the dentist who installed the filling or crown. If some actions were incorrect, then the nerve will make itself felt after a while.
These are the main causes of pulp damage. The symptoms of this condition will be acute. The pulp will begin to react to cold, hot, too spicy, sweet foods. Removing the nerve in such situations is a necessity, despite the fact that minerals and nutrients will stop flowing to the tooth.
How long will a tooth last with and without a nerve?
It all depends on the skill of the doctor, on how competently he assessed the future functionality of the tooth with or without the preserved nerve. If metabolic processes are maintained in the supporting unit (i.e., while the pulp is preserved), then its service life is expected to be longer than that of the pulpless one. When all the conditions on the part of the dentist are met, and the patient treats the restorations with care, then, if the nerve is preserved, the support under the prosthesis can last on average 8-10 years (under a single crown) and about 7 years under an extended structure. If a tooth is “dead,” then its service life is shorter by an average of 30%, i.e. about 5 years.
But if the prosthetics are performed poorly, if the patient does not take good care of the prostheses, then the nerve may become inflamed - and very soon treatment and a new orthopedic design will be required.
How is pain relief performed?
Removal of the nerve takes place under anesthesia. Modern painkillers act quickly and do not harm the patient’s health. In dental practice, both local anesthesia and general anesthesia are used. The first option is applied to the area of the oral cavity in which the tooth is located. The patient is fully conscious. Anesthesia is indicated when the patient, for one reason or another, cannot undergo local injections, or at his own request.
It happens that the patient is afraid of the injection procedure itself. In such cases, the option of preliminary anesthesia of soft tissues by using a spray with an anesthetic composition is provided. After its effect, inserting the needle will not cause pain or inconvenience. Thus, modern dentistry makes it possible to treat teeth without causing discomfort to the patient.
Does the shade of dental tissue change after the procedure?
Does the tooth darken after depulpation? Yes, over time the color will change - it will become gray and lifeless, because the tissues do not receive nutrition from the inside. But the pulpless unit is covered with a prosthesis - so the change in shade will be completely invisible from the outside. If the color of the prosthesis itself has changed, then the reason for this may be the following:
- the use of low-quality materials for manufacturing or non-compliance with its technology,
- staining from coffee, wine, food coloring, tobacco,
- formation of plaque and stone due to poor oral hygiene.
Consequences of nerve removal
If the treatment was carried out by a professional and experienced dentist, then apart from slight pain the patient will not be bothered by anything. Otherwise, there may be such complications:
- a fragment of the instrument remains in the dental canal;
- the nerve was partially removed;
- incorrect or poor-quality filling of the canal;
- mechanical damage to the root or wall;
- rapid darkening of the enamel;
- suppuration due to poor disinfection.
Important! Depulpation at the Crystal clinic is carried out with the minimum possible complications, since all procedures are carried out by certified doctors with extensive experience using high-tech equipment and tools.
After depulpation, it is recommended not to eat for 2-3 hours, not to eat cold, hot, hard or other foods that irritate the mucous membrane. Your doctor will tell you in more detail about the necessary actions after removing the nerve.
What complications may arise
During the process of removing the dental nerve, the following complications may occur:
- perforation of the root wall,
- exit of the instrument or filling mass beyond the root: as a result, periodontitis begins - root inflammation,
- fracture of the instrument in the root canal: such fragments are very difficult to remove, sometimes the entire tooth has to be removed.
Many dentists perform pulp removal only to insure against possible complications after prosthetics - caries or periodontitis. After all, then you will have to remove the prosthesis, treat the tooth, and then make a new prosthesis, because the old one either cannot be removed without damage, or it will not fit on a fresh filling or stump inlay. But let us repeat once again, they will not remove the nerve without clear indications.
Pain in a pulpless tooth
Patients often complain of toothache after depulpation. And everything seems to be done efficiently, but the pain does not go away. It is extremely important to know the reasons why pain appears after nerve removal, as well as what to do in this case.
Causes
There can be several reasons for pain in a “dead” tooth:
- a specific reaction of the body to the procedure of nerve removal and canal filling (the most common and harmless);
- poor quality work performed by the dentist (the canals are not completely cleaned, not all nerves are removed, the canal is poorly sealed, the use of inappropriate filling materials);
- inflammation of the gums, which could arise as a result of injury during treatment;
- pain in the adjacent tooth, which radiates to the pulpless one.
What to do?
If you have a toothache, you should first contact your dentist to determine the cause of the pain. If this is the body’s reaction to canal filling, then the doctor will prescribe additional anti-inflammatory drug therapy, which will help speed up the healing process. If the cause of the pain is poor-quality filling, then the treatment will be much longer and more complex.
Previously, if there was acute pain in a pulpless tooth, it was always recommended to remove it, since its treatment was not possible. Modern treatment methods make it possible to successfully unfill root canals and their further treatment . Other therapeutic and surgical methods of therapy are also applicable. Therefore, you should not delay your visit to the dentist - he will certainly be able to save the tooth and relieve you of pain.
Features of care after removal
Oral care after dental nerve removal and prosthetics must be regular and thorough. Twice a day you need to use a brush and paste, follow the correct cleaning technique (only sweeping movements). It is recommended to rinse your mouth after each meal, and also to exclude toffees, chewing gum, hard pieces of food, and not to chew nut shells or seeds. In order to promptly identify and eliminate dental problems, you should visit an orthopedic dentist at least 1-2 times a year.
“I had a crown placed on a post about 7 years ago. They did it very well and treated it under a microscope. But after the prosthetics, the dentist told me not to forget to come to them every year or every six months for an examination. At the same time, professional hygiene was carried out. I’ve never had any problems in all this time, I eat whatever I want.”
Anna, review from irecommend.ru
Advantages and disadvantages of depulpation
The advantages of tooth depulpation are that it will eliminate or almost completely minimize the risks of pathologies appearing under the prosthesis - it all depends on the skill of the dentist and the patient’s attitude towards the new smile. The disadvantage is that the tooth will become “dead”, i.e. more fragile and with a shorter service life than non-pulpless. But these shortcomings are eliminated, again, by high-quality treatment and materials, and competent care of restorations, as well as the absence of extremely high chewing loads.
How much does depulpation cost?
How much does tooth removal cost? The cost of the procedure ranges from 3000-4000 rubles per 1 tooth in small cities, and in large cities, when treated under a microscope, from 3000-4000 rubles per 1 root canal (there can be 3-4 of them in one tooth). It is more profitable if the clinic offers turnkey installation of the prosthesis - absolutely all manipulations, examinations and materials are included in the total price.
[1] Shashmurina V.R. Biomechanical features of dental depulpation, 2022.
Author: Dulgarov Zh. G. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Indications
The need to remove dental pulp may arise in the presence of an inflammatory process, injuries and periodontal diseases. In this case, the final decision on the procedure is made by the attending physician, who needs to analyze a number of factors - namely, the general health of the patient, age, reasons for the development of the pathological condition, and the presence of concomitant periodontal problems.
Depulpation is carried out in the following cases:
- acute or chronic pulpitis;
- tooth injuries that resulted in a fracture of its crown;
- the presence of residual effects after previously performed pulp removal;
- secondary infection of the pulp and development of inflammation;
- development of complications of cervical caries;
- periodontal lesions near the diseased tooth;
- surgical treatment of dental cysts;
- the need to prepare for further orthopedic or orthodontic treatment.
The final cost of tooth depulpation depends on a number of factors, including the complexity of the procedure. The price of depulping one tooth in dental clinics in Moscow starts from 3,000 rubles and above.