An abnormality such as bone spurs is often ignored until it actively progresses. Patients often come to the clinic late, which entails complex treatment, including surgery. Exostosis is a pathology in which hardened areas of cartilage tissue protrude above the jaw are formed. The causes of this phenomenon are mechanical damage, trauma, tooth extraction and other diseases. Chewing functions are preserved, and soft tissues are also not damaged. But as the protrusions grow, thinning of the mucous membrane and ruptures occur, causing injury to surrounding areas.
Main symptoms
Depending on the specific type, epulis can manifest itself in different ways:
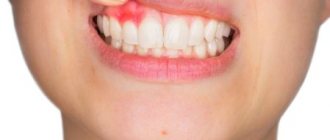
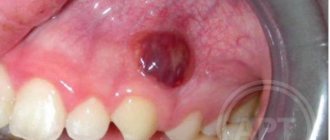
- Fibrous. Doesn't hurt and grows very slowly. The shade of the neoplasm does not differ from the color of the gums. In the absence of therapy, it can reach large sizes.
- Angiomatous. Has a rich purple hue. Causes pain, for example, when chewing food. It is easy to damage during mechanical action (even when brushing your teeth). Sometimes it bleeds.
- Giant cell. The most dangerous type of epulis. Can degenerate into a cancerous tumor. Typical for adults. It has a bright red color, even the slightest palpation causes discomfort.
Based on the stage and age, the growth can be dense or soft, and can range in size from several millimeters to 10 centimeters in diameter.
Wisdom tooth: inflammation of the hood and its symptoms
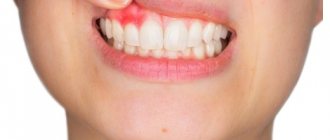
Patients who have inflamed gums near a wisdom tooth usually complain to the doctor that their wisdom tooth is growing, their gums are swollen, and there is also an odor from the wisdom tooth. The formation of an unpleasant odor is caused by the formation of pus, which is gradually released from under the hood. Patients also complain of pain in the area of the wisdom tooth. Such symptoms correspond to only a mild form of pericoronitis.
What do the symptoms of pericoronitis look like in the video? Please note that in the video below you can see the following symptoms: redness and swelling of the hood above the upper wisdom tooth, a small amount of purulent discharge (white) from under the hood. Such symptoms correspond to a mild form of inflammation.
If pericoronitis occurs, treatment is only possible with a dental surgeon. But at the initial stage, patients try to relieve the symptoms on their own using available means: antiseptic rinses, dental drops, painkillers. In most cases, this is ineffective and the inflammation only increases. The following symptoms increase (in various combinations):
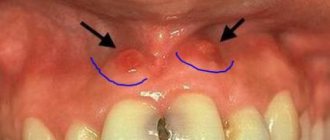
increasing pain- severe swelling and redness of the gums,
- swelling of the cheek (Fig. 4),
- purulent discharge from under the hood,
- painful swallowing
- difficulty opening the mouth,
- increase in body temperature,
- weakness,
- swelling and tenderness of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Important: if at this stage the wisdom tooth hood has not yet been removed (see below), then you should be prepared for the next development of events. Firstly, because inflammation occurs in the area of the masticatory muscles - their spasm can lead to almost complete closure of the mouth. If at this moment you decide to go to the dentist, then he will not be able to do anything for you if your mouth is not opening enough, except to refer you to the hospital.
Secondly, pus may begin to spread not into the oral cavity, but rather deep into the bone and soft tissues, which will cause the formation of an abscess or phlegmon (peripharyngeal or submandibular). The latter complications will also mean inevitable treatment in a hospital, and therefore it is better not to bring the inflammation of the wisdom tooth to a critical level.
How to treat?
Gum treatment should begin as soon as you notice growth. In most cases, you have to resort to surgical intervention, since drug therapy in this case does not have a positive result. The growth is excised under general or local anesthesia. After removal of the epulis, it is recommended to send the biomaterial for histological examination to exclude the malignant nature of the neoplasm.
Next, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to avoid possible complications. For speedy healing, wound healing and antiseptic agents may be prescribed.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the pathology practically does not manifest itself. Symptoms generally have a vague picture, which is why patients rarely see a doctor in a timely manner. But as the condition worsens, the following symptoms appear:
- growths with a pronounced convex shape appear on the tissues; the structure can be embossed or smooth;
- there is a feeling of a foreign object in the mouth;
- pain appears, sometimes quite severe;
- partial jaw dysfunction is observed;
- the shade of the mucous membrane changes to bright;
- capillary obstruction appears in the area of the growth.
Preventive actions
You can prevent damage to the integrity of the gums in the following ways:
- Brush your teeth more carefully, without pressing too hard on the brush.
- Use solid foods with caution.
- Clean the seeds with your hands, not your teeth.
- If there are artificial structures in the mouth, make sure that they do not cause discomfort in the form of rubbing. This mainly applies to removable dentures.
- Use orthodontic wax when wearing braces.
- Carry out dental treatment in a timely manner.
- Do not consume too hot foods or drinks to avoid burns.
- Go to the dentist twice a year to have tartar removed.
Remember that this pathology has a predisposition to relapse. Most often, such cases occur in people who do not follow basic hygiene rules. Be more attentive to the condition of your oral cavity, brush your teeth daily and use additional hygiene products. Be careful not to cause mucosal damage.
Alarming symptoms
If after tooth extraction a white coating with an unpleasant odor appears on the socket, you should consult your doctor. Reasons to contact a specialist are also:
- pain in the mouth,
- pus in the hole,
- continuous bleeding
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- redness and swelling of the gums,
- temperature increase.
If these symptoms appear, you should consult your dentist. The doctor will determine the cause of the problem and eliminate it.
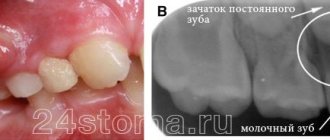
Is there a cyst on the root of a wisdom tooth?
A cyst is a cavity filled with fluid or pus that forms primarily at the apex of the root. It can affect any tooth, including wisdom teeth. Moreover, due to its location and growth characteristics, it is more often susceptible to cystic disease than others. In approximately 40% of cases, figure eights remain completely or partially impacted and grow inside the soft tissue. This is one of the main reasons for the development of neoplasms. Experts identify a separate subtype of it, which is called “follicular wisdom tooth cyst”: it appears on the gum around an unerupted tooth and grows very quickly.
Interesting fact!
A cyst under the upper wisdom teeth will progress faster than under the lower ones. This is because the bone in the upper jaw is more porous, making it easier for infections to spread.
Cyst on a wisdom tooth - what to do?
Conservative treatment of cysts has not proven its effectiveness and is practiced only in a limited number of cases. For example, when surgical intervention is temporarily contraindicated: during pregnancy and breastfeeding, after serious illnesses and operations. Physiotherapy helps to temporarily stop the spread of infection, but is not able to cope with the cyst completely and forever.
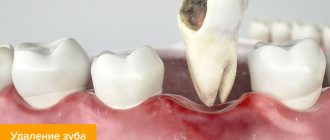
The only effective way to treat a cyst is surgery. The affected wisdom tooth cannot be saved. As a rule, this makes no sense, because “eights” do not play a key role in the chewing process. Therapy will be too complex, time-consuming and expensive, since when a tumor is removed, teeth rarely retain their integrity. Access to the last molar is difficult, and if it is dystopic or partially impacted, sooner or later it will still require extraction. The fact that patients most often discover a cyst too late, when it is no longer possible to save the tooth in any case, also plays a role.
Pericoronitis: treatment
If you have inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth, the treatment most often consists of a dental surgeon removing the hood over the wisdom tooth. However, if severe purulent inflammation is observed, then complete excision of the hood is undesirable immediately, because this can lead to various inflammatory complications.
In case of severe purulent inflammation, the hood is first only dissected to facilitate the outflow of purulent discharge, and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. And the doctor will prescribe you for its complete removal after the active inflammation has subsided. Also, in some cases, the doctor may recommend immediately removing the wisdom tooth (24stoma.ru).
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth –
Removing the hood of a wisdom tooth involves excision of the overhanging mucous membrane over the erupting eighth tooth. Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth leads to the elimination of conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. This minor surgical procedure is usually less traumatic, but in some cases a large amount of gum tissue must be excised.
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth is performed by a dental surgeon under local anesthesia. The procedure is completely painless if you see a good specialist, if the anesthesia is administered correctly and a good anesthetic is used, and not something like novocaine. Pain will appear only after anesthesia has passed (after 30 minutes), so it is worth taking an analgesic even before the pain appears.
- Hood removal: price for 2021 in an economy class clinic in Moscow, a similar service costs about 2,500 rubles. In the regions, the cost of the procedure may be 2 times lower. By the way, in the clinic at your place of residence (if you have an insurance policy and a passport), you should undergo this intervention completely free of charge.
Stages of excision of the hood –
- Conducting local anesthesia,
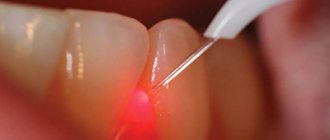
- Using a scalpel and surgical scissors (less commonly, a surgical laser), the dental surgeon excises the gum overhanging the tooth.
- Treating the wound with antiseptics.
- An iodoform turunda is usually placed in place of the excised hood.
- The doctor gives recommendations and schedules a re-examination.
Removing a wisdom tooth hood: video
Please note that both hood excision operations are performed with a surgical laser and not with a scalpel. Using a laser avoids bleeding, swelling and severe pain. In Russian dental clinics, lasers are practically not used (due to their absence), and only a few clinics can boast of their presence.
After the intervention, the following are prescribed:
- Antiseptic baths with chlorhexidine solution 0.05% (3-4 times a day);
- Antibiotics are not prescribed in every case;
- for pain - good tablet analgesics.
Usually this is enough for you to completely forget what wisdom tooth pericoronitis is after 4-5 days.
However, if the doctor performed the operation traumatically, the pain may last for 7-10 days. If you want to remove inflammation as quickly as possible, then after antiseptic rinses, you can additionally apply CholisalGel to the hood 2 times a day in the morning and evening (it has a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect). Remember that if you put gauze soaked in iodoform on the wound surface, you need to remove it yourself no later than the next day. Then it itself will become a breeding ground for infection. After you take out this turunda, it may cover a little. Then it is advisable to treat the wound with a gauze swab soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide.
Important: in some cases, the hood may form again, in which case either a repeat operation may be required, or the issue of tooth extraction will be decided. Often these teeth are in an incorrect position. An experienced doctor can quickly determine the chances of the eighth tooth taking the correct position using an x-ray and external examination of the tooth.
In what cases is it better to immediately remove a tooth with a hood -
If your gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed, the most radical treatment method will be the removal of the 8th tooth, above which the ill-fated hood appears.
This will solve the problem permanently, but you must be prepared for the fact that the eighth teeth may have curved roots (this can be checked by taking a photo) and then removal may be difficult. Situations where deletion is the best solution to the problem -
- Firstly , when the lower jaw is insufficiently long, which means there is not enough space for the eruption of a wisdom tooth. Removal in this case will prevent the remaining teeth from being displaced by the erupting tooth, and will prevent the development of crowding of teeth in the anterior part of the lower jaw.
- Secondly , if the 8th tooth has a strong inclination towards the cheek or the seventh tooth, then it will still have to be removed sooner or later, because it will injure either the buccal mucosa or the root of the 7th tooth, respectively.
For more information about the difficult eruption of wisdom teeth, read the article: → “Features of the growth and eruption of eighth teeth”