Before deciding on dental implantation, the doctor evaluates the volume of bone tissue. If there is a deficiency, a bone grafting operation is recommended, which often frightens the patient and forces him to refuse dental implantation altogether. What should you really be wary of when augmenting bone tissue and is it possible to do dental implantation without it? Are such operations really that scary and are they always necessary? says Dmitry Valerievich Levin, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Chief Physician and Implant Surgeon at the Doctor Levin Center for Private Dentistry in Moscow.
The importance of bone grafting in dentistry
One of the main advantages of implantation over classical prosthetics is that it prevents bone loss in the area of missing teeth. The jawbone constantly needs stimulation, which occurs as a result of the pressure exerted on it during the chewing process. However, after the loss of a tooth, the bone ceases to receive the proper load, as a result of which it begins to decrease. Conventional dentures cannot prevent bone tissue resorption, since they mainly put pressure on neighboring teeth, and not on the area of the missing tooth. Only an implant can stop this natural process. During dental implantation, bone tissue receives the necessary load and does not lose volume, which allows you to avoid numerous negative health consequences and maintain the aesthetics of your smile. In case of prolonged absence of a tooth, as a result of which the jawbone has begun to atrophy, bone grafting comes to the rescue.
What is bone atrophy
Bone atrophy, or loss, is a result of tooth loss. Due to uneven load, the jaw loses volume - in the first year, tissue loss is 25%.
Atrophy can be stimulated by gum disease, endocrine, infectious diseases and the age factor. In patients, the blood supply to the jaw deteriorates, there is a lack of oxygen - the pressure on the tissue changes. The central or spongy layer, which has a porous structure, is subject to the process.
Jaw deformation has different intensity:
- I degree.
The blood supply is not impaired. It is possible to install a classic implant. - II degree.
The mucous membrane contracts. The operation is performed after plastic surgery. - III degree.
The contour is smoothed from the chin and in the oral cavity. Bone augmentation is a must.
The results of the deficiency are expressed in deterioration of speech, changes in facial proportions, and the appearance of wrinkles in the oral area. An advanced degree of atrophy causes displacement of the dentition, loss of adjacent or opposite units. Classical implantation is not possible with bone atrophy.
What is bone grafting for dental implants?
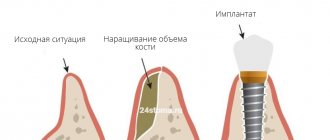
Bone grafting in dental implantology is the augmentation of bone tissue, which is often necessary to perform turnkey dental implantation. On average, 3 to 6 months after the loss of a tooth, the process of bone tissue atrophy begins at the site of its removal, due to the fact that the bone ceases to bear the load. This process reaches its peak after about a year, and if you do not contact an implantologist immediately after removing unhealthy teeth, there is a high probability that additional bone augmentation surgery will be required later. It should be noted that plastic surgery, even in situations where there is a lack of jaw bone tissue, is not always required and not for everyone. The decision on the need for it will be made by the doctor, based on the situation of the individual patient.
There are cases when the bone tissue in the place of a missing tooth remains unchanged for many years, but this is rather an exception to the rule. More often, quite pronounced bone atrophy and even tilting or displacement of teeth towards the defect are observed.
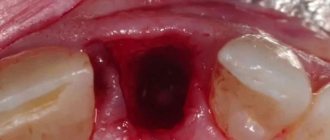
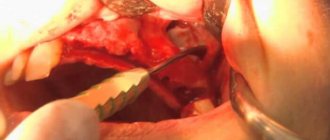
Photos of bone grafting at various stages of its implementation
Overview of methods for growing jaw bone
Bone tissue augmentation before installing dental implants can be carried out using one of four technologies, which we will describe in detail in this section of our article.
Bone tissue augmentation during implantation by splitting the alveolar process
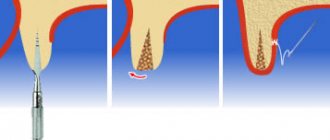
During the operation, the alveolar process, in the area in which bone tissue needs to be built up before implantation, is sawed with a special dental cutter.
The doctor widens and deepens the resulting hole with drills of different diameters. After these manipulations, implants are placed in the prepared bed, and the remaining voids are filled with a synthetic bone filler and covered with a collagen membrane. The wound is sutured and the patient is sent home. Abutments and crowns on implants are installed approximately 4-6 months after bone tissue augmentation surgery combined with implantation. This break in treatment is necessary for the growth of natural bone and the engraftment of the installed artificial roots.
The considered method of bone tissue augmentation during implantation is most often used when it is necessary to install several implants at once and in case of horizontal resorption of the alveolar process, in which the bone has retained a thickness of at least two millimeters. The advantages of the technology include the possibility of combining surgery with the installation of implants, a short period of jaw bone regeneration, and no need to use expensive biological bone material.
The price for bone tissue augmentation in Moscow using the method of splitting the alveolar process starts from 40 thousand rubles. The indicated amount does not include the cost of installing implants.
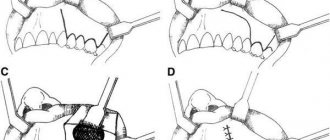
Replanting bone blocks for bone growth
What types of bone grafting are there?
Bone grafting of the lower jaw in the lateral regions is necessary in case of a decrease in the height and width of the alveolar process and a reduction in the distance to the mandibular canal. Significant loss of bone volume in the lower jaw can result in a change from the normal bite to a mesial bite (where the lower jaw moves forward).
Bone grafting of the alveolar process of the upper jaw is associated with bone resorption and the formation of a thin and sharp alveolar ridge. The difficulties of plastic surgery in this area are associated with the task of achieving an optimal cosmetic result.
Bone grafting of the lateral sections of the upper jaw is called sinus lifting, since the maxillary sinuses, or sinuses, are located in this area. There are closed and open sinus lifts, and they differ in the way they penetrate the bone.
Make an appointment
right now!
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Surgeon, Implantologist, Maxillofacial surgeon
Types of bone atrophy in the upper and lower jaw
Destruction of the bone structure of the upper jaw is fraught with injury to the closely localized maxillary sinus. The cells in this area have a loose structure, the bone is thinner, and is actively resorbed in the area of the masticatory elements. When fixing long implants, there is a risk of injury to the sinus membrane, which can stimulate its rupture and the development of sinusitis or chronic runny nose.
The Schroeder classification identifies three types of atrophy of the upper jaws
:
- The jaw tubercles are pronounced, physical abnormalities are not visible, the mucosa is noticeably curved, the palate is deep. Implantation is possible without complications.
- The alveolar processes are not clearly expressed, the palate is of medium depth. Installing implants using the classical method is doubtful, but using a one-stage method is possible.
- The cells are seriously atrophied, the alveolar processes are smooth, the palate is flat, the fold at the level of the palate does not hold its shape. Fixation of classical implants is not possible; it can be done in one stage, depending on the location of the defect.
The tissue of the lower jaw is dense from below and does not decrease so rapidly, but as atrophy progresses, the dentist is faced with the problem of the nearby localized mandibular nerve (it is located under the roots of natural elements). Nerve injury can cause complete or partial loss of sensation in the lower facial part.
According to Keller, there are four types of mandibular atrophy
:
- The tubercles of the alveoli are visible on the jaw, a fold of the mucous membrane is noticeable. You can install classic or one-stage implants.
- The ridge becomes sharper, and muscles are attached at its base. Installation of a classic implant may cause discomfort, but a one-stage implant does not cause complications.
- The jaw of patients with early removed lateral teeth - the alveoli are thinned, the volume in the center does not decrease. It is not possible to implant classical artificial roots; one-stage ones are possible, but there is a fear of the implant shifting when chewing food in case of a single defect.
- In the area of the frontal incisors, the bone is clearly atrophied; the lateral row is not affected. Implantation for such bone tissue atrophy is possible using a combined method.
What materials are used for bone grafting in dentistry?
Both natural and synthetic materials, which have similar capabilities for engraftment and replenishment of bone volume, can be used as a bone tissue implant. Synthetic materials are made based on hydroxyapatite or calcium phosphate. As a rule, they are produced in powder form and are successfully used in world practice.
Autogenic
For bone tissue augmentation, the best material is autogenous, that is, your own bone sections taken from the donor area. Such an area, as a rule, is the chin or the area of the lower jaw in the area of the wisdom teeth. An autogenous graft takes root better than others, but its use is associated with an additional operation to collect donor material.
Allotransplantation
In addition to autotransplantation, in some cases allotransplantation is used, when bone material is taken from another person who bequeathed his organs for medical purposes. In this case, the donor material is carefully selected, sterilized and processed, and the recipient’s body eventually accepts such bone material as its own and successfully restores the lost bone.
Xenotransplantation
When people talk about xenotransplantation, they usually mean the transplantation of bone tissue from animals, usually cattle. The bones of cows and bulls are carefully processed, sterilized, and manipulated to make them compatible with the human body. Such transplants also take root well.
Alloplasty
This is the most modern method, which is most often used by implantologists around the world. The material used is a special bone powder that stimulates tissue growth. This is the least traumatic and patient-friendly method of bone tissue augmentation.
Why does atrophy occur?
Removal of dental bone tissue is not carried out on purpose. Atrophy is almost always the result of a long “downtime” of a certain area of the dentition. Among the factors contributing to the problem:
- advanced inflammatory gum diseases;
- periodontal damage;
- purulent inflammation of the maxillary sinuses;
- acute/chronic pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids and some other medications;
- congenital anomalies of the upper or lower jaw;
- hereditary tendency to the disorder.
But most often, bone tissue subsides after tooth extraction. This is the main cause of the disease. While chewing food, the blood supply to the bone increases. It is due to this that its original volume is preserved. After tearing out the unit, the empty area is no longer subject to the necessary chewing load. Local blood supply deteriorates. Then the bone decreases. In one year, its volume decreases by approximately 25%.
What complications occur during bone grafting surgery?
Bone grafting in dental implantology varies greatly in complexity. This could be a major transplantation of bone blocks or some minor manipulation using osteoplastic material. But any operation requires the skill of a professional and his close attention to each patient individually. Any mistake in the bone tissue augmentation procedure is fraught with complications in the form of wound inflammation, suppuration or rejection of the bone block.
Many consider soft tissue swelling to be a complication after bone grafting. However, this is rather a natural reaction of the body to the surgical intervention. Swelling, as a rule, occurs and increases during the first two to three days, and then gradually subsides. Local hematomas may also appear.
Regardless of the volume of operations, all manipulations must be planned in such a way that the patient can endure them comfortably.
Condition after bone grafting - normal and complications
Within 10 days, unpleasant conditions are possible that accompany any surgical operation and are considered a physiological norm. The intensity of the manifestations depends on the experience of the surgeon, the technologies used, the type of bone grafting, the scope of the operation and the individual characteristics of the body.
Pain
You will not feel pain immediately after the operation; our anesthesiologist will administer an anesthetic along with sedatives. Anxiety may appear towards the end of the day or the next day. The initial intensity of sensations can be completely different, depending on the person’s pain threshold.
To relieve pain, take the medications from the kit you received at the reception. The sensations should completely go away within the first week after surgery.
Bleeding
Bloody discharge may occur during the first 2-3 days. Normally, they should be quite scanty, just tint the saliva a little. The appearance of blood clots or severe bleeding is a reason to immediately visit a doctor.
You can stop the bleeding yourself by pressing the wound surface with a sterile bandage. Avoiding severe bleeding will help avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, in particular acetylsalicylic acid. Some patients, according to indications, are forced to take antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants; it is worth warning the surgeon about this at the stage of preparation for surgery; a corrective plan may be needed.
Edema
Tissue damage and the introduction of osteoplastic material always lead to the development of swelling. It is most pronounced 2-3 days after surgery, then quickly subsides. Swelling can be managed by applying ice compresses. You need to sleep on a large pillow so that your head is elevated.
The swelling goes away by the end of the first week after surgery. Otherwise, there is suspicion of a pathological process of inflammation of the wound surface or deep-lying structures.
Please be extremely attentive to your own condition. For any questionable symptoms, if there is a worsening of discomfort or lack of positive dynamics, consult a doctor. The 24-hour helpline number is located on the post-op advice card .
Is it possible to perform bone augmentation at the same time as dental implantation?
Of course, modern technology for dental implantation suggests that bone grafting of the jaw and installation of an implant can be carried out in one visit, but a lot in this matter depends on the clinical case and the doctor. For example, some specialists try to separate everything: first remove the tooth, then do bone grafting, and only after that carry out implantation. But what is it like for a patient to undergo surgery in the same place several times? Obviously, no one wants to experience this kind of stress. Therefore, bone grafting and implantation should be separated only in extreme cases, when bone tissue is missing in a sufficiently large volume. For the patient, of course, it is preferable to install an implant simultaneously with bone grafting of the jaw, but the decision on the order of the procedures must be made by the doctor, based on the specific case.
One-stage protocol with immediate loading
A one-stage operation is performed if 3 or more teeth are missing. The protocol helps avoid tissue buildup. Single-component (not divided into an abutment and an intraosseous part) implants are installed in the deep layers of bone, which are not subject to resorption. For a larger area of contact between the bone and the titanium root, the product is fixed at an angle, identifying areas of bone tissue that are less susceptible to atrophy.
The implant is implanted using a minimally invasive method: it is screwed through a puncture in the gum. The top of the artificial root (abutment) rises above the gum - the dentures are installed immediately after implantation (on 2-3 days). After a year, the lightweight adaptive prosthesis is replaced with a permanent one.
1
Implantation
Implantation of 8-12 implants into deep bone layers (without bone grafting)
2 - 3 days
2
Prosthetics
Fixation of an adaptive prosthesis with a titanium arch and metal-plastic crowns
in a year
Permanent prosthetics
One-stage dental implantation for abnormal bone deficiency (less than 2.5 mm) is impossible without tissue augmentation. The operation is not performed for large maxillary sinuses, which cannot be avoided when installing implants at an angle.
Among the complexes of the one-step protocol:
- All-on-4.
The technique is used if the patient is missing all the teeth on the jaw. The dentition is restored using 4 implants (2 in the smile area and 2 on the sides). To avoid complications, “all-on-4” implantation for atrophy of the bone tissue of the upper jaw is carried out with caution, taking into account the close location of the maxillary sinuses. - All-on-6.
A modernized version of the All-on-4 method (implantation for severe bone deficiency). The increased number of supports (6 instead of 4) expands the scope of application of the method and allows for more stable fixation of the structure. - Basal implantation.
The method is used for acute bone loss. Suitable for missing three or more teeth in a row. For complete edentia, 8-12 implants are used on one row of teeth. They are fixed into the deep layers of the jaw bone.
All-on-4 and all-on-6 protocols involve the use of surgical templates to determine the location of the implant, without taking into account the condition of the bone. With basal implantation, templates can be dispensed with; this expands the scope of application of the technique. Implantologists at the ROOTT Clinic, using computed tomography, select suitable jaw sites for fixation with sufficient bone volume. If circumstances require it, a couple of additional implants are installed free of charge - if one of the titanium roots does not take root, there are enough implants left for prosthetics.
What prices can you expect for bone grafting in dentistry?
As a rule, the cost of bone grafting of the lower or upper jaw directly depends on the quantity and quality of the required bone material. Let's say, prices for a closed sinus lift in Moscow start from 15,000 rubles, for an open one - from 25,000 rubles, and taking your own bone material costs around 30,000 rubles. Each case is unique, and how much your bone grafting will cost will only be known at an appointment with a specialist.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru