Types of pathology
There are several types of maxillary sinus cysts:
- Odontogenic. The inflammatory process forms in the root system of an untreated dental unit located on the upper jaw. As the tumor increases in size, it destroys the bone and grows into the sinuses. The contents of the cyst are purulent.
- Retention. The reason for the development is dysfunction and obstruction of the glands responsible for the production of mucus.
False cysts are classified into a separate category. In such formations there are no epithelial cells. The appearance of such formations is due to a violation of the structure of the maxillofacial apparatus.
Paranasal sinus cyst - symptoms and treatment
Treatment depends on the type of cyst, its location and size. If it is less than 1 cm and there is no discharge, then the doctor suggests conservative methods: regular examination, tablets, sprays and drops. If the cyst is large or there is purulent discharge, then surgery will be required.
Drug treatment of cysts
The method allows you to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and causes of cyst formation: swelling, inflammation and blockage of the sinus anastomosis. Drug treatment is effective and can alleviate the patient's condition in the early stages of the disease. However, it will not help when the fibrous membrane of the cyst has become too dense.
Drugs used:
- vasoconstrictor drops - quickly reduce swelling in the anastomosis area and normalize ventilation of the sinuses of the nasal cavity; medications in this group are addictive and can be safely used for no more than 5 days in a row;
- antihistamines - will help if the cyst is caused by allergies;
- mucolytics - normalize the outflow of mucus;
- antiseptics - help fight inflammation and cleanse the surface of the nasal mucosa;
- topical glucocorticosteroids are most effective in the treatment of allergic rhinosinusopathy, prolonged sinusitis, hyperplasia of the mucous membrane in the area of the anastomosis and ostiomeatal complex;
- painkillers - reduce pain caused by the pressure of the cyst on surrounding tissues [6];
- probiotics - normalize the microflora of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx, which is important in the treatment of chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Surgery
Indications:
- cyst more than 8 mm;
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- signs of suppuration inside the cyst [7].
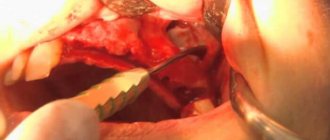
The most popular method of treating cysts is puncture or puncture. The surgeon pierces the wall of the cyst with a thin needle and pumps out the purulent discharge [1]. However, this method only has a temporary effect. Piercing the cyst, as well as spontaneous leakage of its contents, relieves pain for a while. But gradually the cyst grows together again and begins to accumulate purulent fluid. To remove it completely, more serious surgery will be required [8].
Maxillary sinusotomy according to Caldwell-Luke
It is performed through an incision under the upper lip in the mouth. This is a classic method for removing sinus cysts, but now it is practically not used due to its high morbidity: after the operation, scars, adhesions can form and the functioning of the sinuses can be disrupted.
Microsinusrotomy
A minimally invasive surgical technique that is performed through the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus. A 4–8 mm hole is formed in the bone, and the cyst is removed with special instruments. Performed under general anesthesia. The disadvantage is the risk of damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve and the formation of persistent facial neuralgia.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS surgery)
This method is considered the most gentle and effective: during the procedure, unnecessary incisions and punctures are not made on the patient’s face. It is performed through the nasal cavity under endoscopic control. Allows you to reach all paranasal sinuses, including the sphenoid, frontal sinuses and cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. The operation is performed under local and general anesthesia [17].
Additional benefits:
- can be used to treat children;
- reduce the likelihood of cyst recurrence;
- you need to stay in the hospital for no more than two days;
- the incision heals quickly;
- the operation leaves no scars;
- there is no risk that adhesions will appear [18].
Relative disadvantages: trained specialists and special equipment are required, which makes the operation expensive.
Causes
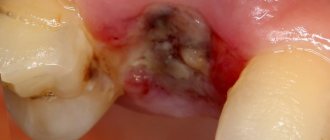
The key reason for the formation of a maxillary sinus cyst is dental disease. Especially when treatment was not carried out or performed poorly. Pathology develops against the background of advanced caries, periodontitis and pulpitis on chewing units. This is due to anatomical features. Premolars and molars are located closest to the paranasal sinuses and are separated from them by a thin septum.
Until recently, teeth with cysts were subjected to extraction. Today, dentists prefer to perform organ-preserving surgeries. All stages of work are performed under control using a dental microscope.
An endodontist removes the cyst, performs sterilization and filling of the canals.
The formation of a tumor can be caused by a deviated nasal septum, jaw abnormalities, or chronic blockage of the ducts of the nasal glands due to rhinitis or sinusitis.
Diagnosis of the disease
A neoplasm measuring up to 15 mm is diagnosed only with a CT scan. A dentist can suspect the presence of a pathology during a routine examination of the patient’s oral cavity based on existing complaints.
Clinical symptoms
As the cyst grows, the patient develops alarming symptoms similar to those of acute sinusitis. These include:
- acute headache;
- chronic nasal congestion;
- clear or yellow nasal discharge;
- a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the area under the eyes;
- the presence of a viscous mucous lump in the throat after waking up.
Clinical symptoms become more pronounced as the lumen in the nasal cavity closes. If there are concomitant dental problems, pain in the tooth and swelling of the gums occur.
Potential Complications
If left untreated, the infection spreads to adjacent teeth in the upper jaw. There is a risk of bone deformation or jaw fracture, the development of an abscess, phlegmon and other purulent complications.
The cyst is accompanied by sinusitis and chronic sinusitis. The growth of the tumor is dangerous due to visual impairment. The formation of a purulent cyst can lead to the development of meningitis or encephalitis.
Complex treatment
When treating pathology, dentists use medicinal and surgical techniques. The tumor is removed during surgery. Further drug therapy is designed to eliminate the symptoms of the inflammatory process and prevent complications.
Treatment in dentistry
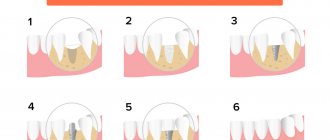
Most patients go to the dentist when the size of the cyst exceeds 1 cm. The dental surgeon removes the bag of pus by cystectomy or cystotomy. The choice of technique is based on the size of the cyst and clinical indications.
The dentist is faced with a number of tasks:
- remove the source of inflammation in the oral cavity and stop the inflammatory process;
- provide drainage for the outflow of pus;
- if possible, save the diseased tooth;
- fill the resulting cavity with bone material;
- close the fistula between the oral cavity and the sinus.
Inpatient treatment in the ENT department
If the appearance of a cyst is caused by ENT pathologies, you should consult an otolaryngologist. Tumors are removed by surgery, laser or gentle endoscopic techniques. During endoscopy, the doctor gains access to the affected area through the nasal passages or an opening in the facial wall of the maxillary sinus. Control of manipulations on the monitor screen is carried out.
conclusions
The most objective way to diagnose dense space-occupying formations of the upper jaw is computed tomography (CBCT or MSCT).
If signs of osteoma are detected in the cavity of the upper jaw, the patient must be recommended to undergo surgical excision of the formation. Morphological verification of the removed material is mandatory.
The combination of an endoscopic transnasal approach and navigation equipment in the removal of osteomas of the upper jaw is the most modern and optimal option for treating the pathology.
MestaMidin-nos has proven itself in local therapy as a means to prevent possible postoperative infectious and inflammatory complications. The use of MestaMidin-nos allows you to avoid a course of systemic antibacterial therapy.
The publication was carried out with the support of Solopharm in accordance with internal policy and current legislation of the Russian Federation.
What kind of disease is this
In general, a cyst is a benign formation, similar to a cavity, with contents inside the walls.
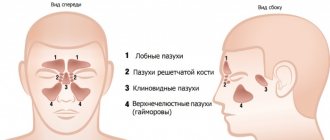
In addition to the maxillary, it is often found in the sinuses near the nose, but under no circumstances does it extend beyond these zones. The cyst can be of any size - from small formations in the initial stages to large ones that expand if treatment is started.
There are two mechanisms for the development of education:
- Retention , which occurs and develops if the excretory duct of the glands in the mucous membrane is blocked.
- Odontogenic , progressing as a dental pathology, i.e. due to diseases of teeth and gums.
Both single and multiple cysts can also be detected. In some people this formation is acquired, while in others it is present from birth.
This is a very common disease: according to statistics, in every fifth person, a detailed examination of the nose can reveal a small maxillary sinus cyst (MSC). Such formation does not make itself felt for a long time, or manifests itself in the form of pain and unpleasant symptoms.
The patient who has been diagnosed with a cyst is being monitored dynamically. If his condition worsens sharply, surgical intervention is possible.
ENT about a cyst in the sinus:
ICD code
There are two disease codes according to the ICD:
- 8
- K09
Each of them is assigned depending on how the cyst was formed and what type it acquired.
How to identify a cyst in the maxillary sinus?
Since cystic cavities are benign neoplasms, they do not cause any systemic manifestations. The local clinical picture manifests itself several months after the onset of the pathological process. But even its occurrence does not always become a reason to go to the doctor. Most often, maxillary sinus cysts are discovered by a dentist during a preliminary examination to perform a sinus lift or implantation.
The main clinical manifestations of cysts in the maxillary sinus:
- Painful sensations in the infraorbital region of a pressing nature (pain intensifies when changing body position);
- Discharge from the nasal passages is purulent or mucopurulent in nature, the amount of which depends on the presence and severity of the inflammatory process;
- Gradually increasing facial asymmetry (when the cyst reaches a large volume);
- Constant exacerbations of infectious lesions of the maxillary sinus;
- Swelling of the nasal passages (severe nasal congestion);
- Pain in the upper jaw (as well as: a characteristic crunch when pressed or loaded);
- Headaches (most often in the forehead or temples).
The clinical picture of cystic formations is practically indistinguishable from acute sinusitis, so doctors always differentiate these two pathologies using instrumental studies. For dental specialists, it is especially important to make the correct diagnosis, since the presence of a cyst is not always a contraindication for sinus lifting, but an acute infection does not allow surgical intervention.
Identification of cystic formations occurs by performing x-rays of the sinuses or in the process of studying the bones of the skull on a computed tomography scan. Additionally, an endoscopic examination may be prescribed, which is both diagnostic and therapeutic. Histological examination using targeted biopsy is mandatory, which allows us to have an idea of the origin of the tumor and exclude malignant oncology.
What is a cyst in the maxillary sinus called?
A maxillary sinus cyst is a benign formation that has a hollow structure containing fluid inside. Cysts of the maxillary sinuses are quite common, but are almost always found at random. Their location and origin may differ, which will determine the characteristics of the clinic and even treatment.
Odontogenic cyst
Among the many benign tumors of the jaw tissue, the cyst is found most often and represents a pathology quite dangerous for the bone structure. Odontogenic formations in the vast majority of cases remain undiagnosed for a long time, and therefore reach enormous sizes. The growth of the cyst provokes atrophic processes in the bone tissue, which thins, becomes fragile, and then disappears completely.
Such formations are characterized by a long latent course until the cavity grows to gigantic proportions. Then a characteristic crunch begins to be noted in the jaw, especially during chewing loads. Ignoring the problem leads to spontaneous fractures of the jaw, compression of the maxillary sinus with disruption of its functions, exacerbation of the inflammatory process with damage to the structures of the maxillary sinus and the formation of sinusitis.
Tooth cyst growing into the maxillary sinus
Damage to the dental canal involving the root and surrounding tissues is a consequence of an infectious process of bacterial origin. In the absence of adequate and timely treatment, a gradual delimitation of the inflammatory reaction from healthy tissues by a wave of cellular structures occurs.
This creates a cavity called a dental cyst. It gradually increases and destroys the bone tissue of the jaw. When localized in the anterior part of the upper jaw, gradual penetration into the maxillary sinus occurs.
Retention
The most common form of neoplasm in the maxillary sinus, which is also called a true cyst. It is located in the lower wall of the sinus and has an epithelial lining - a distinctive feature of true cystic cavities. The formation is clearly determined by X-ray examination randomly, as it does not manifest itself clinically.
When the cyst reaches a significant size, problems begin with the functioning of the maxillary sinus. The structure and physiology of the microvasculature is disrupted, resulting in the formation of edema. This symptom is manifested by nasal congestion, often without pronounced discharge from it. Due to the lack of specificity of the clinical picture, even the presence of subjective signs of the disease is not a reason to consult a doctor.
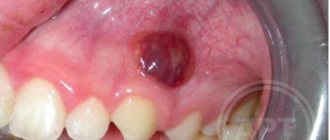
Perforation discovered after the fact
If the patient suffered discomfort in the first 2-4 weeks and did not contact the dentist, who, in turn, did not identify the problem at the time of its occurrence, the perforated wound turns into a permanent fistula that is not prone to healing.
Typical signs of chronic sinusitis appear:
- the nose on the side of the fistula is constantly stuffy;
- the parasinus area gives off a dull pain, its waves can roll to the nearest eye and temple;
- pus is discharged from the nostrils and in the mouth (from the fistula);
- possible swelling of the cheek on the side of the fistula with visible deformation of the face.
In most cases, a fistula is felt as air passing between the nose and mouth while talking or sneezing. Pronunciation of a number of sounds becomes more difficult. Liquid food may enter the nose from the mouth. Therapy for an old fistula shows rather weak results, and relapse with such a problem is not uncommon. There is no alternative to surgical intervention - it is necessary to open the maxillary sinus, remove foreign objects and non-viable tissue. The fistula requires excision throughout its entire thickness, the defect is closed with healthy tissues of the patient. After the operation, an antibiotic course lasting one and a half to two weeks is prescribed; in parallel, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs must be used.