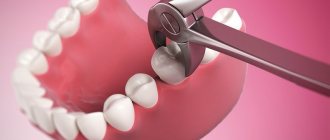
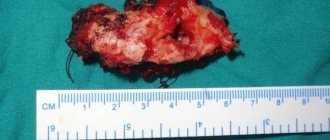
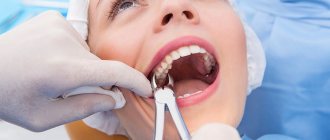
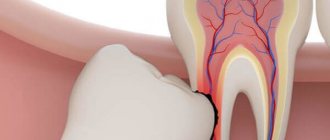
Wisdom teeth often cause dental problems, the most serious of which is an atypical position. “Eights” can grow at an angle, be completely embedded in bone tissue, or only partially erupt.
With their crown, they can injure a neighboring tooth. When such situations arise, dentists recommend atypical wisdom tooth extraction. Timely surgery will help avoid injuries and the occurrence of carious inflammation. Specialists at the Profident Junior surgical dentistry clinic will perform the operation as quickly and painlessly as possible.
When is root removal required?
It happens that only the root remains in the gum, and its crown part has been completely lost due to mechanical stress or untreated caries. After an X-ray examination, CELT specialists determine the possibility of treating such roots and their further use as a support for the crown. If this is not possible and the tissue surrounding the root is changed, a decision is made to remove it. Indications for root removal of front, broken, baby and other teeth are:
| Indications | Reasons for deletion |
| Serious damage to the crown of the tooth | Complete fracture of the crown, complex transverse fracture, fracture along the lobar axis, as well as destruction of the tooth crown below the gum level |
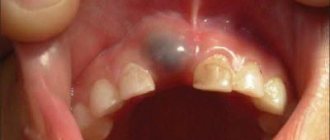
| Inflammatory processes | Development of inflammation in the root area in the form of a cyst, granuloma, abscess or phlegmon |
| Dentofacial anomaly | The tooth that is to be removed has an atypical location and prevents other teeth from growing, injures the gums and causes discomfort |
| Movable root | Third degree of tooth mobility |
It is worth noting that the crown part of the tooth can be destroyed both on a tooth with a nerve and on a pulpless tooth. If the tooth is “alive” and the destruction of its coronal part is not severe, its preservation is quite possible. As for a tooth with a removed root, the latter, as a rule, are seriously damaged and their restoration is quite difficult. In this case, the doctor may recommend removal of the tooth root and subsequent implantation.
Causes of dystopia
Dental dystopia develops under the influence of various factors, the main ones being:
- deviations in the normal growth of the jaw (delayed growth);
- discrepancy between the size of the teeth and the size of the jaw;
- partial adentia (absence of some teeth);
- deviations in teething;
- hyperdentia (supernumerary teeth);
- atypical anlage of tooth germs;
- significant discrepancy between the sizes of temporary and permanent teeth;
- macrodentia (increase in the size of the dental crown);
- abnormal arrangement of adjacent teeth;
- injuries of tooth buds;
- bad habits (hand biting, thumb sucking by children during sleep);
- early removal of baby teeth and lack of rational prosthetics;
- narrowing of the dentition;
- late loss of baby teeth;
- genetic predisposition;
- absence of a neighboring tooth or an antagonist tooth on the opposite jaw;
- odontogenic neoplasms (cysts, tumors).
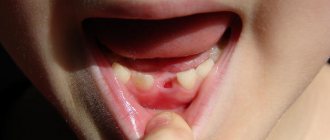
Removing the root of a decayed tooth
Cases where a root remains after tooth extraction are not uncommon. Its removal is a difficult and unpleasant procedure for the patient, even despite the effectiveness of modern anesthesia. Fortunately, the need to remove tooth roots does not always arise. If the root is healthy enough, it is treated and prosthetics are performed. However, removing a rotten tooth root is simply necessary, since its preservation will entail a number of problems:
- Halitosis (bad breath);
- A breeding ground for infection in the oral cavity, possible damage to neighboring teeth;
- The appearance of subgingival stone;
- Spread of infection to the maxillary sinuses, development of osteomyelitis;
- The appearance of cysts and granulomas at its apex ( removing a tooth with a cyst on the root
is a complex procedure); - A decrease in the body’s overall immunity due to the fact that it is forced to constantly fight the source of inflammation.
In order to properly plan the operation, our dentist performs an x-ray examination. The operation itself is performed using local anesthesia, dental forceps or an elevator. Removing the roots of the front teeth
is carried out using rotational movements, and lateral movements using rocking. The most complex cases may require additional manipulations, the use of burs and special microsurgical dental instruments. Removing the roots of the teeth of the lower and upper jaw is a more complex procedure than removing a whole tooth. It requires special training, which consists of examination, diagnosis and sanitation of the oral cavity. The treatment plan is drawn up based on diagnostic studies and the patient’s indications.
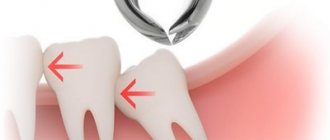
Dystopic wisdom tooth: what is it?
A dystopic tooth is one with an incorrect location relative to the entire dentition, which may extend beyond the border of the alveolar processes. As a rule, such an anomaly can be predicted in childhood and appropriate therapeutic or preventive measures can be taken. In the case of wisdom teeth, this is more difficult to do, since the rudiments of eights form much later than those of other teeth. Moreover, pathology can harm neighboring teeth, so when a specialist discovers a dystopic wisdom tooth, the question of its removal is almost always raised. Symptoms of a dystopic wisdom tooth usually manifest themselves in the form of inflammation and pain.
Root removal steps:
- Carrying out activities for the administration of a local anesthetic drug;
- Separation of the circular ligament from the neck of the tooth, moving the gum tissue away from the edge of the alveolus;
- Cutting the gums and drilling out the bone tissue to provide access to the root (if necessary);
- The process of removing the root using forceps or a dental elevator. If a tooth has several roots, removal is carried out in parts;
- Treatment of the hole, suturing (if the gum is cut), treatment of the operated area.
It is important to understand that removing roots located on the upper jaw is different from removing roots located on the lower jaw. In the first case, special forceps are used, in the second - elevators. The technique for removing the roots of the upper jaw involves twisting single roots and dislocating parts of one root. As for the roots of the lower jaw, they are twisted.
Duration of healing of the dental alveoli
Many doctors' clients are interested in how long it will take for the dental alveolus to heal after the removal of a damaged tooth. Typically, this process takes from 5 to 7 days. After 3-4 weeks, the gum area adjacent to the socket heals completely. It is important that the jaw is not damaged during the removal process. Such an injury will cause the healing process to take six months. To prevent this from happening, make an appointment at the As-Praktika clinic, where experienced dental surgeons work. In Samara, the price for tooth extraction is quite reasonable; this procedure is available to absolutely everyone. You can make an appointment at this clinic online by indicating the desired date of visit.
How much does tooth root removal cost in Moscow?
The cost of tooth root removal is determined individually, as it depends on how complex the case is. In the dental department of the multidisciplinary clinic CELT, it starts from 800 rubles for a simple removal and ends at 10,000 rubles for a complex removal of a 2nd degree dystopic tooth. You can view our basic prices in this section of our website. In order to find out the exact cost of tooth root removal in our clinic in Moscow, consult our specialist.
In the dentistry of the CELT clinic, you can get a consultation with a dental surgeon, undergo an examination and remove the roots of the teeth, if there are indications for this. We will eliminate any dental problems effectively and absolutely safely.
Atypical extraction of the 8th tooth, complicated at the Profident Junior clinic
Complex and atypical tooth extractions at the Profident Junior clinic are performed using the latest equipment and reliable instruments. Specialists use European techniques that make it possible to painlessly and quickly perform any type of surgical operation, including the removal of a wisdom tooth with cutting of the gums.
Atypical tooth extraction, depending on the complexity, is performed using local or general anesthesia. The staff ensures sterilization and cleanliness to ensure safety during treatment.
You can find out the price for atypical wisdom tooth extraction at the Profident Junior clinic by scheduling a consultation.
This can be done not only by phone, but also online by filling out a simple form on the website. Here the uniform is blue.
Profident Junior uses all methods of atypical tooth extraction. Dental surgeons have the necessary skills and constantly improve their qualifications.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Tooth root removal
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Types of wisdom teeth dystopia
All types of dental dystopia differ in the position of the tooth relative to the dentition. Diagnosis of pathology is carried out by a dentist-therapist or an orthodontist. To determine the type and characteristics of pathology in dentistry, an orthopantomogram is used, as well as targeted x-rays.
| Type of dystopic tooth | Description |
| Medial impacted tooth | The tooth protrudes forward (from the outside of the dentition). |
| Distal impacted tooth | The tooth protrudes backwards (from the inside of the dentition). |
| Angular dystopic tooth | An impacted tooth is located at an angle in relation to neighboring teeth. |
| Tortoposition | The tooth is rotated around its axis |
| Horizontal impacted dystopic tooth | The impacted dystopic tooth is located horizontally relative to the dentition. |
| Reverse dystopic impacted tooth (rare) | The root part is located at the top, and the coronal part at the bottom (in the bone tissue). |
Impacted dystopic wisdom teeth are the most difficult case. The tooth not only has an incorrect position, but also has problems with eruption. Retention can be either partial (part of the tooth is visible on the surface) or complete (the tooth is completely hidden in the soft tissues).
Impacted and dystopic teeth – is there a difference?
The standard assumption is that a person should have 32 teeth, but it is now common for people to have fewer teeth. The most common example is the absence of two or more eights in the dentition. At the same time, the computed tomogram shows that they are, in principle, there, but they are located deep in the jaw. There are other situations: individual units have partially grown, but not enough to be considered full-fledged teeth. Such teeth are called incompletely erupted or partially impacted.
In dental practice, there is another type of anomalies of eruption and position - dystopia. This is when the tooth has grown “to its full height”, but in the wrong direction - towards the brothers in front; to the right, towards the cheek, or to the left, towards the palate or tongue. In some cases, this state of affairs interferes with neighboring teeth and can cause various diseases in them, in others it harms the person himself, worsening the quality of chewing food, making it impossible to properly close the jaws, curving the entire dentition and causing pain.
In addition, incomplete eruption and dystopia are often combined with each other, and then the situation worsens so much that it leaves the dentist practically no choice - such an abnormal tooth must inevitably be removed.
Rehabilitation after atypical wisdom tooth extraction
After 10-14 days, the patient's stitches are removed. Until this moment (until the gums heal), the patient should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid overheating your body. Avoid hot baths, saunas and sunbathing for a while. Also avoid strenuous exercise, as this increases the chance of bleeding from the wound.
- Rinse your mouth with solutions prescribed by your doctor.
- Chew food in the area opposite the area being operated on.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor, such as anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
In what cases is removal necessary?
Invasive intervention can be carried out urgently (it is necessary to urgently provide assistance to the patient) and routinely. In what cases is a tooth removed (indications for manipulation):
| Planned operations | Emergency indications |
| Destruction of the crown in which it is impossible to save the unit | Acute purulent inflammation complicated by periostitis, odontogenic osteomyelitis |
| Supernumerary segment or its retention in the jaw (retention) | Exacerbation of chronic inflammation in periodontal tissues |
| Atypical position of wisdom teeth | Abscess |
| High mobility of units in periodontitis | Phlegmon |
| Cyst, granuloma of the apical zone | Lymphadenitis |
| Removal of the root element (six or seventh), if it interferes with orthopedic, orthodontic treatment, implantation | Jaw injury |
| Extraction of the milk element (prevents the eruption of the permanent segment) | |
| Tumors of the jaw |
Models of forceps for tooth extraction
To pull out a specific tooth, you need to use a specific model of forceps:
| Unit location | Purpose and types of forceps |
| Canine, maxillary incisor | For the anterior segment, forceps with narrowed cheeks and straight ones are used. |
| Maxillary premolars | S-shaped forceps with wide cheeks are used to extract the first or second chewing segment |
| First, second molars from above | There are two types of such a tool: for the right and left sides. On one of the cheeks there is a spike-like protrusion, on the other there is a groove with a rounded tip. |
| Third molars | To remove wisdom teeth, use bayonet-shaped pliers. The cheeks are identical, wide, and have a concave groove. |
| Lower incisors | For the lower front elements, a beak-shaped tool with a narrow working surface is used. |
| Canines, premolars of the lower jaw | Wide beak-shaped forceps with grooves. |
| Removing a root or its fragment (top) | Forceps with thin narrow cheeks (when closed, their ends touch) |
| Molars from below | S-shaped, with a spike on one side, the second surface is rounded. |
| Lower third molars | Flat tweezers. |
When is it necessary to remove an impacted tooth?
Despite millions of years of evolution, humans still continue to develop and improve. Our ancestors had massive jaws, and therefore they accommodated more teeth, which were adapted for biting and tearing food, as well as for chewing it. Now, due to changes in diet, the jaws have begun to shrink, and therefore sometimes there is simply not enough space for all the teeth. This is how impacted teeth appear, i.e. teeth, the rudiments of which formed in the jaw, but there was not enough space for them to erupt, and therefore they remained in the bone, never growing into the dentition.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of dystopic teeth consists of examining the oral cavity, assessing the bite and obtaining x-ray data. To accurately determine the condition of teeth and jaws, use:
- Teleradiography - X-ray examination is carried out from a large focal length, which reduces the radiation dose to the patient and reduces distortions in the image. Teleradiography is needed not only for diagnostics, but also for predicting the results of treatment and monitoring its process.
- Computed tomography is a layer-by-layer study of tissue. The images are combined into a 3D image, which allows you to more accurately study the position of the tooth in the jaw and develop a treatment plan.
- Orthopantomography - provides a detailed image of the jaw and all teeth, allows you to evaluate the inclination of erupted and impacted teeth, and detect anomalies of tooth germs and hard tissues.
How can you remove a tooth located deep in the jaw?
The doctor carefully prepares for the operation of removing an impacted tooth, because This is obviously a more complex manipulation. The less of the crown part has come out from under the gums, the more trouble there will be. It is no coincidence that they say: the most difficult thing is removing an impacted dystopic tooth. Not only does it need to be exposed and freed from the bone, but it also needs to be removed in such a way that no small parts remain in the jaw. But first things first.
Before surgery, the patient is always sent for a CT scan. The information from this examination allows the doctor to understand the location and depth of the tooth, whether it has contacts with neighboring units, the location and shape of the roots, proximity to the nerves of the jaw and other important anatomical structures. Only after this can you plan the course of the operation, the type of anesthesia, the required instruments and auxiliary equipment.
A few words about pain relief methods when removing impacted teeth. In general, they are not much different from those with simpler and less labor-intensive removals. It is believed that these operations are somewhat more traumatic and take a long time. Not at the Refformat clinic. With us you will quickly part with your wisdom teeth. Therefore, you should not be scared, but if you are very scared of dentists in general, we can offer the option of treatment in your sleep. You can find out what this method is here and here.
The patient does not require special preparation, however, in cases where the operation will be performed under sedation, he should first undergo a small set of tests and consult with a therapist.
After the onset of anesthesia, an incision is made in the gum exactly above the place where the causative tooth lies, which provides access to the periosteum and jaw bone. The dissected tissues are carefully pulled apart. Then they proceed according to one of the options - either they drill out the bone around the tooth in order to remove it entirely, or the tooth is divided into parts with burs and removed in parts. The method of removing impacted and dystopic teeth in some cases involves filing down the crown part, and then dividing and extracting the roots. If a nerve passes near the coronae, a coronotomy can be performed - removing only the supragingival part of the tooth, while the roots will remain in place.
The operation ends with returning the soft tissue flaps to their place and suturing the wound with nylon or self-absorbing threads. To prevent postoperative complications, the doctor may inject an anti-inflammatory drug into the transitional fold, as well as prescribe antibiotics for up to 5 days.
If the sutures were applied with synthetic threads, they are usually removed after a week and a half. There is no need to remove catgut sutures.