To the reference book Enlarged lymph nodes signal the development of an inflammatory pathology in the body or may be a consequence of excessive growth of lymphoid tissues (lymphoproliferative diseases, hyperreactivity of the immune system).
Author:
- Oganesyan Tigran Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
4.00 (Votes: 10)
Lymph nodes are peripheral organs of the lymphatic system, the main task of which is to provide a natural filter for lymph and the body's immune defense. In the lymph nodes, lymphatic fluid is filtered from microorganisms, atypical cells and other antigenically foreign particles. In this case, an immunological reaction develops, during which the formation and maturation of immune cells that are capable of destroying foreign agents (bacteria, fungi, viruses, parasites, malignant cells, foreign inclusions) occurs.
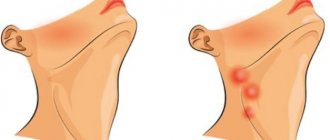
Enlarged lymph nodes signal the development of an inflammatory pathology in the body or may be a consequence of excessive growth of lymphoid tissues (lymphoproliferative diseases, hyperreactivity of the immune system).
Inflammation of the lymph nodes can be purulent and non-purulent, depending on the duration of the course - acute and chronic. It can be local (when only a certain group of nodes increases) and generalized (inflammation affects several unrelated groups at once).
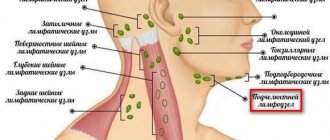
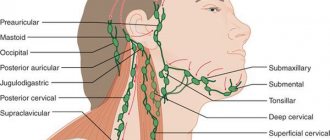
Depending on their location, all lymph nodes are combined into the following regional groups:
- cervical, widely scattered along the front and side surfaces of the neck;
- mental, located behind the chin;
- occipital, located at the junction of the neck and skull;
- submandibular, lying in the middle of the lower jaw;
- parotid and behind the ear, located in front and behind the ears;
- axillary, one group of which is located in the thickness of the fiber of the axillary region, and the other is adjacent to the inner surface of the pectoral muscles;
- elbow – on the front surface of the elbow joint;
- inguinal, located in the inguinal folds;
- popliteal, localized on the back surface of the knee joints.
Thus, there are quite a lot of areas where enlarged lymph nodes can be detected. Moreover, with different diseases they increase in different ways. The following may differ: consistency, surface structure, mobility, pain on palpation, and the condition of the skin over them. It is very important to diagnose and identify the root cause of the development of the inflammatory process, which only a certified doctor can handle.
General information
The organs of the lymphatic system play a protective role in the human body. They serve as a barrier to viruses, bacteria, and also filter out harmful substances. In total, there are more than 450 lymph nodes in the adult body, and their maximum number is formed by the age of 10.
Lymph nodes are connected by lymphatic vessels - lymph (a fluid with a high content of lymphocytes, or “white blood cells”) circulates through them. Produced in the bone marrow, lymphocytes circulate throughout the body, first passing through the spleen and then the lymph nodes. Thanks to this, they gain the ability to produce antibodies to destroy microbes. Source: A.G. Rumyantsev, professor, V.M. Chernov, professor, V.M. Delyagin, professor Enlarged lymph node syndrome as a pediatric problem Practical Medicine, 2007, No. 5 (24), pp. 12-15
When an infection enters , a kind of “attack” is carried out on it, as a result of which the lymph nodes can enlarge (during this period they more actively produce antibodies). After recovery, the nodes return to normal size. If their diameter and density do not return to their original state, the child must be shown to a doctor.
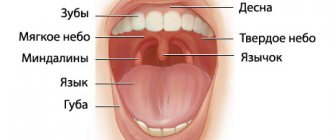
What are lymph nodes in the neck
Lymph nodes are bean-shaped and ribbon-shaped formations of lymphatic tissue. In the neck, the nodes are located in clusters of up to 10 pieces, near blood vessels, mainly large veins. Their surface is represented by connective tissue, which forms a capsule. Trabeculae extend from it into the node, also connective tissue - the so-called supporting structures, similar to beams.
The internal structural basis of the node is a stroma of reticular connective tissue with process cells. These cells, together with the reticular fibers they form, form a three-dimensional network. The structure of the stroma also includes phagocytic cells of several varieties. The inner part of the ganglion is called the medulla. Closer to the plane of the capsule is the cortex with a superficial part and a zone of deep cortex.
The accumulation of lymphoid tissue inside the space of the node forms follicles - lymph nodes located closer to the capsule. The deep cortex contains a large number of lymphocytes with a dense and uniform arrangement. The lymph node, in fact, is a barrier to retain infection, pathologically altered cells, and tumors. It contains the formation of lymphocytes - protective cells that destroy foreign elements. Cervical lymph nodes are divided into:
- anterior cervical
- posterior cervical;
- occipital;
- chin;
- submandibular nodes.
In a normal state, a healthy person often cannot feel them, since they are small in size, soft and elastic, and quite mobile under the skin.
Indicators of normal lymph nodes:
- diameter up to approximately 5 mm;
- soft consistency;
- single location, that is, lack of connection with each other or with the skin;
- absence of pain upon palpation (palpation);
- mobility.
Reasons for enlargement and main groups of lymph nodes
| Group of lymph nodes | Typical reasons for the increase |
| Parotid | Pyoderma (inflammation of the scalp accompanied by pus), inflammation of the outer or middle ear, the presence of lice, atopic dermatitis, eczema. |
| Occipital | Various inflammations in the scalp, fungal diseases, rubella, etc. |
| Submental | Abscess of the jaw, inflammation of the lower lip, damage to the front teeth, stomatitis. |
| Submandibular | Gingivitis, stomatitis, dental damage. |
| Cervical (in the direction of the muscles at the back of the neck) | Sore throat, chronic tonsillitis, tuberculosis of the tonsils, adenoids, infectious form of mononucleosis. |
| Cervical (middle) | Scarlet fever, tonsillitis, “cat scratch disease”, Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma ( important - these are malignant oncological processes!), toxoplasmosis. |
| Cervical (lateral) | Tumors, lymph node tuberculosis, nasopharyngeal infections. |
| Elbow | Infections of the forearm or hand. |
| Axillary | Shoulder or arm infections, vaccine reactions, cat scratch disease. |
| Inguinal | Infections of the skin, bones and muscles of the lower extremities, inflammation of the joints, dermatitis, inflammatory processes in the genitals, reaction to a vaccine introduced into the femoral area. |
Antibiotics and surgery for lymphadenitis
If a bacterial infection enters the patient's body or purulent complications develop, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. If the lymph nodes in the neck are swollen and the temperature is significantly higher than 36.6º C, this is probably the case. The patient must remain in bed, drink a sufficient amount of warm liquid and take vitamin complexes.
The ineffectiveness of drug therapy and UHF procedures is often the reason for making fundamental changes in treatment tactics. In case of serious purulent inflammation, the surgeon may prescribe an operation, the main purpose of which is to clear the clogged lymph node channel.
Oncological alertness
Lymph nodes are often enlarged due to lymphogranulomatosis (Hodgkin's lymphoma) or lymphosarcoma (non-Hodgkin's lymphoma). These are malignant processes that are manifested by increased density, painlessness and large diameter of the lymph nodes in the absence of other reasons for their deformation. Lymph nodes enlarge in groups, asymmetrically (for example, on one side of the neck). At the initial stage of the process, their mobility and separate arrangement are maintained. If the oncological process continues without treatment, the lymph nodes may become fused, and moderate pain rarely occurs. Source: N.V. Nagornaya, E.V. Vilchevskaya, A.P. Luachak, E.N. Marchenko, E.V. Bordyugova, A.P. Koval Hodgkin's disease (lymphogranulomatosis) in children // Child's Health, 2013, No. 1 (44), pp. 13-15
Symptoms that require consultation with a doctor are enlarged lymph nodes:
- more than 7 days;
- more than 1 group;
- accompanied by elevated body temperature;
- in a child under one year old;
- progressive over time;
- with changes in local skin.
3. Diseases leading to inflammation of the lymph nodes
If the lymph nodes become inflamed and enlarged in more than one area of the body, it is called generalized lymphadenopathy.
This inflammation of the lymph nodes is caused by:
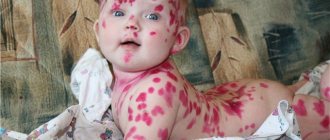
- Viral diseases such as measles, rubella, chickenpox or mumps;
- Mononucleosis, the symptoms of which are fever, sore throat, fatigue, as well as the viral infection cytomegalovirus that causes similar symptoms;
- Bacterial diseases such as strep throat (caused by streptococcus bacteria) or Lyme disease (a bacterial infection spread by certain types of ticks);
- Side effects from taking phenytoin, a medicine used to prevent seizures;
- Side effects from the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine;
- Cancer - leukemia, Hodgkin's disease and lymphoma;
- AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome;
- Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Diagnostic methods
After examination and collection of complaints and medical history, the specialist sends the child for a general examination . It includes x-rays, blood and urine tests . Additionally, the following studies may be needed:
- blood serology;
- diagnosis of tuberculosis;
- lymph node biopsy followed by cytological examination in the laboratory;
- Ultrasound.
Sometimes children are prescribed antibacterial drugs as part of the diagnosis. Based on their effectiveness, they confirm or refute the bacterial nature of the disease.
Why is lymph node dissection performed?
Malignant tumors are distinguished by their ability to form metastases, spreading beyond the primary focus and beginning to develop in other organs and tissues. Cancer cells separate from the primary tumor and spread throughout the body through the blood and lymph, including the lymph nodes themselves, first the closest ones.
Therefore, removal of the lymph nodes along with the primary tumor makes it possible to stop and even prevent the development of metastases. The results of the study of nodes removed during lymph node dissection help in drawing up an optimal program for further treatment. Thus, lymph node dissection combines directly therapeutic and diagnostic functions.
Treatment methods
Enlarged lymph nodes are not an independent disease, but a symptom of some other disease. Therefore, therapy in this case comes down to eliminating the root cause of this reaction. The rate at which nodes return to normal size varies, depending on the severity and type of underlying disease.
If a child gets sick very often, then immunomodulators are recommended to strengthen the body's defenses. The choice of drug should be made only by a doctor.
Important! Enlarged lymph nodes should not be heated - this can lead to the development of suppuration and blood poisoning! Any self-medication is prohibited - the reason and type of therapy is determined by a specialist.
Probable causes of lymphadenitis
As already mentioned, if the lymph node in the neck is swollen, the first thing to do is to look for the cause. Inflammation within the lymphatic system may indicate the presence of a disease within its boundaries, or may be a symptom of another pathology.
Doctors consider the most common factors causing pain and swelling in the neck and lymph nodes to be:
- Entry into the body of pathogenic bacteria that provoke infectious diseases. The most commonly diagnosed in this case are ARVI, influenza, oral pathologies (stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, pulpitis), as well as chickenpox, rubella, sore throat, etc.
- Malfunctions of the immune system. An increased number of potentially dangerous microorganisms is associated with the latent course of chronic illnesses, serious hypothermia, and a lack of vitamins and minerals necessary for full life. Stress can also negatively affect the immune system.
- Acquired human immunodeficiency virus.
- Malignant degeneration of lymphatic cells.
- Mechanical damage and injury to the node or surrounding tissues.
Advantages of contacting SM-Clinic
“SM-Clinic” is a team of some of the best specialists in St. Petersburg, advanced diagnostic equipment and comfortable conditions. We have no queues, all examinations are carried out quickly, appointments are conducted by highly qualified doctors.
If your child has enlarged lymph nodes in the neck or in any other area, you should urgently contact a specialist for diagnosis and treatment. Delay in some cases is very dangerous!
To make an appointment with a pediatrician, immunologist or other pediatric specialist, call us.
Sources:
- A.G. Rumyantsev, professor, V.M. Chernov, professor, V.M. Delyagin, professor. Syndrome of enlarged lymph nodes as a pediatric problem // Practical Medicine, 2007, No. 5 (24), pp. 12-15.
- N.V. Nagornaya, E.V. Vilchevskaya, A.P. Luachak, E.N. Marchenko, E.V. Bordyugova, A.P. Koval. Hodgkin's disease (lymphogranulomatosis) in children // Child's Health, 2013, No. 1 (44), pp. 13-15.
Grek Elena Anatolyevna Clinic
Author of the article
Grek Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor of the highest qualification category
Specialty: immunologist
Experience: 24 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
How to make an appointment with a specialist in oncology
To get a consultation with a specialist in our oncology center, you need to use any convenient recording method. Fill out the online form on the website, entering all the required data, or call us at the contact number.
Onko is open for you not only on weekdays, but also on weekends, so you can choose an appointment time that is convenient for you. We are located on 2nd Tverskoy-Yamsky Lane, 10, close to the Tverskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Chekhovskaya, Belorusskaya and Mayakovskaya metro stations. Take care of your health and consult a doctor on time, without waiting for your condition to worsen.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |
Is it possible to cure lymphadenitis with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine promises to alleviate the symptoms of lymphadenitis and eliminate maximum discomfort that began when the lymph node in the neck became swollen. Even doctors cannot speak unequivocally about the benefits or harms of such therapy. It is believed that the weak effectiveness of folk recipes is fully justified by their harmlessness and naturalness (in the absence of an allergic reaction).
Although such methods will not cure the disease, certified doctors often prescribe home remedies for patients with lymphadenitis as a concomitant therapy. And yet you need to be extremely careful with them, because they can both speed up the healing process and delay it.
The most effective recipes, judging by the opinions and reviews of Internet users, are presented below:
- Echinacea tincture is considered one of the best antiseptic natural preparations. You can buy it at any pharmacy. It is taken orally. This product belongs to the category of inexpensive drugs.
- Applying a healing stone – green jadeite – to enlarged lymph nodes. Supporters of alternative medicine truly believe that its energy will help the patient recover.
- Rinse with herbal decoction. You will need chamomile, mint and calendula collections. You need to gargle with the decoction several times a day.
- For rinsing, you can use classic ingredients that are found in any kitchen: salt and soda. For 1 glass of water you will need half a teaspoon of both components. Gargle every 2-3 hours.
- Freshly squeezed agave juice. People also believe that aloe vera will help cure inflamed lymph nodes. It is recommended to take it orally, 1 tbsp. l.
Prevention for adults and children
To prevent inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck, it will not be possible to follow a specific step-by-step scheme. The disease, the causes of which lie in one thing - weakened immunity, can be prevented if:
- constantly strengthen the body's immune forces;
- cure all pathologies of an infectious nature to the end, do not neglect them;
- do not be in drafts and avoid hypothermia;
- to harden;
- protect yourself from injuries and bruises;
- prevent infection of open wounds;
- do not neglect the rules of personal hygiene and wear gauze bandages during an epidemic.
Nutrition plays an important role in maintaining immunity: it should be rational, include eating a lot of vegetables and as little fatty, fried foods, chips, sparkling water, etc. as possible.
About lymph
The lymphatic system consists of lymph nodes and the vessels that feed them. It is multifunctional, but its main function is to protect the body from various pathogens.
For this purpose, immune cells exist in the lymph nodes - T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes.
The passage of blood through small capillaries creates a plasma filtration effect. Some of the blood enters the surrounding tissues, and some goes back into the bloodstream. Another one - into the vessels. The result is the formation of lymph. It is a clear, watery liquid containing immune cells.
Lymphatic vessels, uniting, enter the thoracic lymphatic ducts, right and left, the same, in turn, flow into the veins. This results in the return of fluid to the bloodstream.
Lymph nodes, as part of the body's immune system, are located in different parts of the body. Their task is to be filters, a kind of barriers for infectious carriers and pathogenic cells.