Causes of inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve
Factors contributing to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve are:
- surgical interventions on the jaw bones;
- fractures of the base of the skull, lower and upper jaws;
- tumors;
- complex tooth extraction;
- hypothermia;
- surgery on the maxillary sinus;
- improperly administered anesthesia;
- incorrectly performed dental prosthetics;
- metabolic disorders;
- the presence of foreign bodies that irritate the nerve trunk or injure nerve endings;
- bacterial or viral infection;
- various types of intoxication of the body;
- hypovitaminosis;
- weakening of the immune system.
Causes of inflammation
Primary neuritis of the facial nerve occurs due to:
- hypothermia of the face, cold, wind, drafts;
- insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the nerve.
Secondary neuritis of the facial nerve is caused by the following reasons:
- inflammatory diseases of the ear: otitis media, eustachitis, mastoiditis;
- infections: mumps virus, measles, herpes;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- vascular disorders - for example, atherosclerosis of the vertebral arteries;
- brain tumors;
- anesthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve by the dentist.
Other factors that provoke inflammation include:
- traveling on a bus or minibus next to an open window;
- long work under air conditioning;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- endocrine diseases - for example, diabetes;
- hypertension, intoxication of the body;
- nervous stress, emotional instability.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis
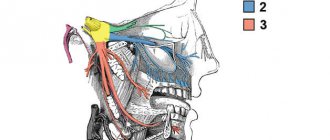
The maxillary trigeminal nerve consists of three types of nerve fibers:
- vegetative;
- motor;
- sensitive.
The symptomatic picture of neuritis may vary depending on which fibers were affected by the inflammatory process.
Damage to sensory fibers
In particular, with inflammation of the sensory fibers, the patient may complain of a tingling sensation, numbness, and weakened sensitivity in the area innervated by the trigeminal nerve.
Damage to motor fibers
When motor fibers are damaged, there is a partial or complete decrease in strength in the innervated muscles, their atrophy and deterioration of tendon reflexes.
Damage to vegetative fibers
When the vegetative fibers are inflamed, the patient experiences cyanosis and swelling of the skin, dryness and thinning of the skin, and the potential risk of developing a trophic ulcer increases.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the facial nerve
If the doctor is properly qualified, then only based on the patient’s complaints will he be able to make a diagnosis and identify the severity of the pathological process. But even if the clinical picture is typical, the patient will have to undergo a series of diagnostic examinations:
- take blood and urine tests;
- undergo magnetic resonance imaging;
- do electroneurography.
The results obtained will help determine what treatment for inflammation of the facial nerve will be. In addition, such an examination will allow the doctor to identify the body’s perception of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - these are the drugs that will be used for therapy.
Pain due to inflammation
In addition, a disease such as inflammation or neuritis of the facial trigeminal nerve makes itself felt with attacks of pain of a very diverse nature:
- cutting,
- burning,
- pricking,
- tearing
- shooting, etc.
In this case, the area of pain does not always correspond to the area of innervation and can spread to the lower jaw, cheeks and chin.
Pain may be accompanied by:
- muscle spasms (facial, chewing),
- the appearance of nasal discharge,
- development of hypersalivation,
- increased lacrimation.
Lack of sensation in the tongue, lips and chin
With inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve, not only the entire nerve can be damaged, but also its individual branches. This is why numbness and pain can occur in various areas of the face. For example, when the lingual branch of the nerve is inflamed, patients complain of pain and sensitivity disturbances in the anterior part of the tongue, and when the mental branch is damaged, in the area of the lips and chin.
Pain when laughing, chewing, brushing teeth and shaving
Pain due to neuritis of the maxillary trigeminal nerve can intensify with touching, chewing, laughing and with changes in temperature. That is why patients, trying to prevent the recurrence of painful attacks, avoid excessive mobility and prolonged conversations, and refuse brushing their teeth and shaving.
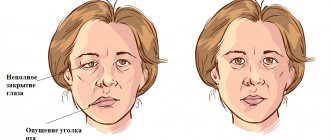
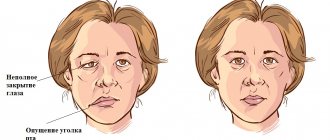
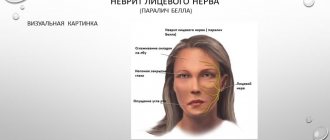
How does neuritis of the facial nerve appear?
Neuritis of the facial nerve can begin with mild pain in the ear area. Simultaneously with the onset of pain or after a couple of days, the facial muscles partially or completely lose mobility. The patient's face becomes distorted, the affected part freezes in the mask.
With timely treatment, the patient has a great chance of recovery - in 75% of cases the disease goes away completely. If facial paralysis does not resolve within three months, the patient's chances of making a full recovery are greatly reduced.
In order for facial neuritis to pass without consequences, you need to consult a doctor in the first hours after the onset of symptoms.
Treatment of neuritis of the maxillary trigeminal nerve
Therapy
The treatment program for trigeminal neuritis is drawn up taking into account the causes of the disease and its clinical signs. The main goals of treatment are:
- achieving a sensitizing effect;
- fight against bacterial and viral infection;
- increasing the body's immune forces;
- elimination of swelling of the nerve trunk;
- restoration of natural adaptive and compensatory reactions;
- normalization of the patency of nerve impulses.
Healing procedures
The set of procedures aimed at blocking the inflammatory process and eliminating all manifestations of neuritis includes:
- antibacterial therapy;
- antiviral therapy;
- elimination of factors contributing to the occurrence of intoxication;
- removal of tumor-like neoplasms or dissection of adhesions compressing the nerve;
- prescribing vitamin and mineral complexes to the patient;
- stimulation of nerves and muscles;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, UHF, ultrasound, paraffin therapy).
People suffering from trigeminal neuritis are advised to regularly visit dental clinics and have their oral cavity sanitized.
Examination for facial nerve disease - find and eliminate the cause of the disease
The symptoms of facial nerve pain are almost the same in all cases, but its causes are different and require different treatments. Treatment “blindly” can delay the healing process. Therefore, in our clinic everything starts with searching for the exact cause and location of the nerve damage.
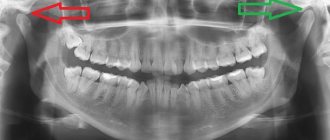
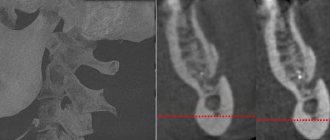
MRI of the brain, temporal bone. MRI scans show the brain centers of the facial nerve and its area of exit (root) to the base of the brain, blood vessels, and temporal bone. Circulatory disorders, cysts and tumors are easily recognized.
Blood tests to check for infections, biochemical changes that damage the facial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a favorite area of attack by the herpes virus group. The suspicion of the presence of the virus and its activity can be easily verified using a blood test.
Electromyography, Blink reflex - measurement of electrical potentials of facial muscles. Helps assess the function of impulse transmission along the facial nerve, the degree of its impairment, judge the effectiveness of treatment, the presence of complications, and help in choosing the correct treatment tactics.
Stimulation electromyography of the facial nerve (electroneuromyography, myography of the facial nerve)
Clinical manifestations of neuralgia
The following symptoms are characteristic of trigeminal neuralgia:
- attacks of severe pain;
- increased pain during any actions with the mouth (chewing, opening, etc.);
- facial distortion;
- concentration of pain in the eyes, ears, teeth, mouth;
- teak.
Trigeminal facial neuralgia is characterized by attacks of stabbing, cutting, pulling pain lasting up to 1 minute. In the vast majority of cases, one side of the face is affected, but there are cases when pathological processes spread to the entire face. Painful sensations can be projected into the teeth and can cause the removal of a completely healthy tooth.
Symptoms
The main characteristic symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is paroxysmal pain. It comes suddenly and in its intensity and speed of spread resembles an electric shock. Typically, intense pain forces the patient to freeze in place, waiting for relief. The attack can last from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes, after which there is a period of calm. The next wave of pain may come within hours, days, weeks or months.
Over time, the duration of each attack of neuralgia increases, and periods of calm are reduced until a continuous aching pain develops.
The provoking factor is irritation of trigger points:
- lips;
- wings of the nose;
- eyebrow area;
- middle part of the chin;
- cheeks;
- area of the external auditory canal;
- oral cavity;
- temporomandibular joint.
A person often provokes an attack when performing hygiene procedures (combing hair, caring for the oral cavity), chewing, laughing, talking, yawning, etc.
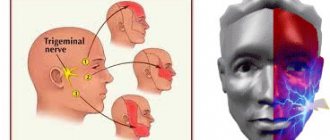
Depending on the location of the lesion, the pain takes over:
- the upper half of the head, temple, orbit or nose if the ophthalmic branch of the nerve is affected;
- cheeks, lips, upper jaw – if the maxillary branch is affected;
- chin, lower jaw, as well as the area in front of the ear - with neuralgia of the mandibular branch.
If the lesion affects all three branches or the nerve itself before it is divided, the pain spreads to the entire corresponding half of the face.
Painful sensations are accompanied by other sensory disturbances: numbness, tingling or crawling sensations. Hyperacusis (increased hearing sensitivity) may be observed on the affected side.
Since the trigeminal nerve contains not only sensory, but also motor pathways for the transmission of impulses, with neuralgia the corresponding symptoms are observed:
- twitching of facial muscles;
- spasms of the muscles of the eyelids, masticatory muscles;
The third group of manifestations of neuralgia are trophic disorders. They are associated with a sharp deterioration in blood circulation and lymph outflow. The skin becomes dry, begins to peel, and wrinkles appear. Local graying and even hair loss in the affected area is observed. Not only the scalp suffers, but also the eyebrows and eyelashes. Impaired blood supply to the gums leads to the development of periodontal disease. At the time of the attack, the patient notes lacrimation and drooling, swelling of the facial tissues.
Constant spasms of muscle fibers on the diseased side lead to facial asymmetry: narrowing of the palpebral fissure, drooping of the upper eyelid and eyebrow, upward movement of the corner of the mouth on the healthy side or drooping on the diseased side.
The patient himself gradually becomes nervous and irritable, and often limits himself to food, since chewing can cause another attack.
Causes
Most often, inflammation of the facial nerve forms at the junction of the trigeminal nerve trunk with the brain stem, where pressure on the nerve of a blood vessel can occur and disease can form. Another of the most common causes is a local formation (aneurysm, tumor) that compresses the facial nerve. Also the culprits of the disease may be:
- inflammatory processes in the mouth, nose, ears;
- physical impact on the face, injuries;
- diabetes;
- intoxication;
- nervous disorders;
- hypothermia;
- hypertensive crisis.
The nerve can be damaged during dental or plastic surgery. Sometimes neuralgia can be one of the signs of multiple sclerosis.
Types of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is divided into two types. The first, the so-called true trigeminal neuralgia, is a holistic disease caused in most cases by compression of the nerve or disruption of the blood supply. The second type - secondary trigeminal neuralgia - is a symptom of a general disease of the body. It could be a tumor or a serious infection.
In most cases, doctors diagnose inflammation of one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve, but in some situations inflammation of two or three processes occurs at once. Inflammation can affect either one side of the face or both, and in different combinations.
Treatment of neuralgia
Treatment of neuralgia is a long and difficult process, but doctors at the CELT Pain Clinic know how to carry it out with maximum positive effect. For this purpose it is used for the treatment method.
Conservative method
Conservative treatment involves taking medications:
- antispasmodics;
- anticonvulsants
Radiofrequency rhizotomy
- Cost: 35,000 rub.
- Duration: 15-30 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2 hours in hospital
More details
It is very important to correctly calculate the dosage of medications and take them regularly, since this is the only way to achieve the desired effect. It is equally important to regularly attend physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Bernard currents;
- acupuncture;
- paraffin applications.
If this treatment method does not bring the desired effect, the attending physician may decide on surgical treatment.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If you or your relative are bothered by severe pain in one or another part of the face, the neurologists of the Health Energy clinic will come to the rescue. We will conduct a full diagnosis to identify the causes of the pathology and prescribe comprehensive treatment. At your service:
- modern drug regimens to reduce the frequency and intensity of attacks;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, etc.;
- delicate therapeutic massage;
- acupuncture;
- help from a psychologist if necessary.